PPPoE LAC Subscriber Bringup in cnBNG
Introduction
Test In this tutorial we will learn how to bring-up PPPoE LAC subscriber session in Cloud Native BNG (cnBNG). We will configure this lab to have both LAC and PTA sessions on same access interface. Whether the session is PTA or it is LAC will be decided by Radius attributes sent during auth.
Topology
The setup used for this tutorial is shown in figure 1. This setup uses Spirent to emulate client and L2TP Network Server (LNS). Spirent port 1/2 will be used for client emulation: PTA and LAC on same port. Which connects to the Access Network Provider ASR9k BNG UP node. LNS is emulated by Spirent port 1/1. When client tries to connect on ASR9k BNG UP, cnBNG CP authenticates the client with AAA server. Based on attribues received in Access Accept from Radius, client is either terminated as PTA session on cnBNG or as LAC session on cnBNG.
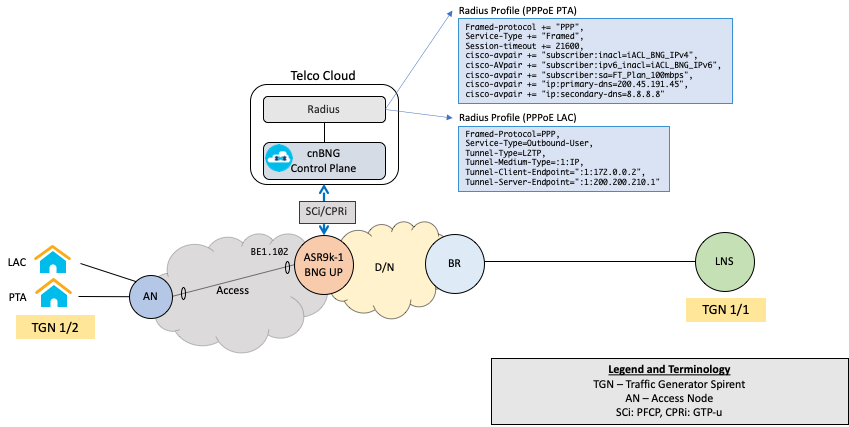
Prerequisite
Make sure l2tp-tunnel endpoint is configured in cnBNG CP Ops-Center and the corresponding POD is running for LAC sessions to work.
instance instance-id 1
endpoint l2tp-tunnel
exit
exit
Verify l2tp-tunnel POD is running on K8s Master VM:
cisco@cnbng-tme-lab-aio-cp:~$ kubectl get pods -n bng-bng | grep l2tp
bng-l2tp-tunnel-n0-0 1/1 Running 1 22h
cnBNG CP Configuration
cnBNG CP Configuration has following constructs/parts for PPPoE:
- IPAM (applicable for PTA only)
- Profile PPPoE
- Profile DHCP (applicable for PTA only)
- Profile AAA
- Profile Radius
- Profile Feature-Template
- Profile L2TP
- Profile Subscriber
- User-Plane
Let’s understand each one step-by-step and apply in Ops Center in config mode.
IPAM
This is optional for PPPoE LAC only profile. IPAM defines subscriber address pools for IPv4, IPv6 (NA) and IPv6 (PD). These are the pools from which PPPoE PTA CPE will get the IPs. IPAM assigns addresses dynamically by splitting address pools into smaller chunks and then associating each chunk with a user-plane. The pools get freed up dynamically and re-allocated to different user-planes on need basis.
ipam
instance 1
source local
address-pool pool-ISP1
vrf-name default
ipv4
split-size
per-cache 262144
per-dp 262144
exit
address-range 20.0.0.1 20.0.255.254
exit
ipv6
address-ranges
split-size
per-cache 262144
per-dp 262144
exit
address-range 2001::1 2001::1:100
exit
prefix-ranges
split-size
per-cache 65536
per-dp 65536
exit
prefix-range 2001:1:: length 48
prefix-range 2001:2:: length 48
exit
exit
exit
exit
Profile PPPoE
This profile is same as the BBA Group which was defined on ASR9k integrated BNG solution. We define service names etc. For this tutorial we will keep it simple and only specify the MTU.
profile pppoe ppp1
mtu 1494
exit
Profile DHCP
Incase of PPPoE DS PTA subscribers we will be using the DHCPv6 server to assign the IPv6 (IANA+IAPD) prefixes to CPE. For this example we will have cnBNG CP act as a DHCP server to assign IPv6 addresses to CPE/subscribers. In profile DHCP we define the DHCP server and which IPAM pool to use by default for subscriber. We can use different pools for IPv4, IPv6 (IANA) and IPv6 (IAPD).
profile dhcp dhcp-server1
ipv4
mode server
server
pool-name pool-ISP1
dns-servers [ 8.8.8.8 ]
lease days 1
exit
exit
ipv6
mode server
server
iana-pool-name pool-ISP1
iapd-pool-name pool-ISP1
lease days 1
exit
exit
exit
Note: The definition of IPv4 server profile is not needed for PPPoE subscribers. For PPPoE subscribers IPv4 addresses will be assigned by IPCP using IPAM directly.
Profile AAA
This profile defines the AAA parameters, like which Radius group to be used for authentication/authorization and accounting. In this tutorial we will be using radius group defined as “local” under radius profile for authentication and accounting.
profile aaa aaa_pppoe-1
authentication
method-order [ local ]
exit
accounting
method-order [ local ]
exit
exit
Profile Radius
Under this profile, Radius groups are created.
profile server-group local
radius-group local
exit
profile radius
algorithm round-robin
deadtime 3
detect-dead-server response-timeout 60
max-retry 2
timeout 5
!!! Radius server IP and port definitions for auth and acct
server 192.168.107.152 1812
type auth
secret cisco
exit
server 192.168.107.152 1813
type acct
secret cisco
exit
attribute
nas-identifier CISCO-BNG
!!! This should be protocol VIP to reach Radius
nas-ip 192.168.107.165
exit
server-group local
server auth 192.168.107.152 1812
exit
server acct 192.168.107.152 1813
exit
exit
exit
!!! we can also set COA client
profile coa
client 192.168.107.152
server-key cisco
exit
exit
Profile Feature-template
This profile defines subscriber feature template. This is the template which will be applied to dynamic subscriber interface. We also enable service/ session accounting here.
profile feature-template pppoe-1
vrf-name default
ipv4
mtu 1500
exit
session-accounting
enable
aaa-profile aaa_pppoe-1
periodic-interval 1800
exit
ppp
authentication [ pap chap ]
!!! will use IPAM pool-ISP1 for IPv4 address assignment using IPCP, this is not required for LAC only profile
ipcp peer-address-pool pool-ISP1
ipcp renegotiation ignore
ipv6cp renegotiation ignore
lcp renegotiation ignore
max-bad-auth 4
max-failure 5
timeout absolute 1440
timeout authentication 5
timeout retry 4
!!! the following command will offload PPP keepalives to cnBNG UP
keepalive interval 30 retry 5
exit
exit
We can also define service profiles using feature-template, which gets applied on per subscriber session. The service profile in case of radius can be applied during authentication/authorization using service activate attribute or it can also be applied using CoA.
profile feature-template FT_Plan_100mbps
qos
in-policy PM_Plan_100mbps_input
out-policy PM_Plan_100mbps_output
exit
exit
Note: In above policy-map PM_Plan_100mbps_input and PM_Plan_100mbps_output are expected to be defined on userplane.
Note: cnBNG currently doesnot support QoS policies for LAC sessions. These policies are expected to be applied on LNS.
Profile L2TP
This profile defines the l2tp parameters for LAC sessions. L2TP Tunnel source and destination IPs along with authentication and other parameters are defined under this profile.
profile l2tp lac-1
mode lac
!!! This is hostname which will be used for tunnel authentication
hostname lns.cisco.com
hello-interval 600
retransmit initial timeout max 8
retransmit initial timeout min 4
retransmit initial retries 5
retransmit timeout max 8
retransmit timeout min 4
retransmit retries 10
receive-window 1024
vrf default
authentication
tunnel timeout no-session 10
tx-connect-speed 100000
rx-connect-speed 100000
tunnel-load-balancing equal
!!! This is password which will be used for tunnel authentication
password cisco
ipv4 df-bit reflect
!!! This is tunnel source IP, usually this is the loopback IP of ASR9k UP which is reachable from LNS
ipv4 source 172.0.0.2
!!! This is tunnel destination IP reachable from ASR9k UP and is the IP of LNS
ipv4 destination 200.200.210.1
exit
Profile Subscriber
This profile can be attached on per access port level or per user-plane level. This profile for PPPoE defines which dhcp server profile to apply for IPv6 address assignment, along with feature-template, pppoe-profile and aaa-profile to be used for auth/acct.
profile subscriber subscriber-profile_pppoe-1
dhcp-profile dhcp-server1
pppoe-profile ppp1
session-type ipv4v6
l2tp-profile lac-1
activate-feature-templates [ pppoe-1 ]
event session-activate
aaa authenticate aaa_pppoe
exit
exit
User-plane
This construct define the association configs. Peering IP as well as subscriber profile to be attached to user-plane or at port level. In this tutorial we will attach subscriber profile at port level.
user-plane ASR9k-1
!!! this should be the IP of ASR9k to which this control-plane will peer with
peer-address ipv4 192.168.107.142
!!! the port-id here is the ASR9k access port or interface name
port-id Bundle-Ether1.102
subscriber-profile subscriber-profile_pppoe-1
exit
exit
cnBNG UP Configuration
UP Configuration has mainly four constructs for cnBNG
- Association Configuration
- DHCP Configuration
- Access Interface
- Feature definitions: QoS, ACL
Association Configuration
This is where we define association settings between cnBNG CP and UP. The auto-loopback with “secondary-address-upadte enable” will allow dynamic IP address allocations using IPAM for PTA sessions.
cnbng-nal location 0/RSP0/CPU0
hostidentifier ASR9k-1
!!! cnBNG UP routable IP (may be loopback or direct interface IP) used for peering with cnBNG CP
up-server ipv4 192.168.107.142 vrf default
!!! cnBNG CP IP (generally protocol VIP) used for peering with cnBNG UP
cp-server primary ipv4 192.168.107.165
auto-loopback vrf default
interface Loopback1
!!! Any dummy IP
primary-address 1.1.1.1
!
!
cp-association retry-count 5
l2tp enable
secondary-address-update enable
!
Note: NAL stands for Network Adaptation Layer for Cloud Native BNG in IOS-XR
Note: cnBNG CP and UP doesnot require to be on same LAN, they need L3 connectivity for peering
We need to create a Loopback for cnBNG internal use on ASR9k.
interface Loopback1
ipv6 enable
DHCP Configuration
This is where we associate access interfaces with cnBNG DHCP profile. cnBNG specific DHCP profile makes sure DHCP packets are punted to cnBNG CP through CPRi/GTP-u tunnel. Since PPPoE PTA subscribers use IPCP for IPv4 address assignment, dhcp ipv4 profile is not needed for PPPoE PTA subscribers.
dhcp ipv6
profile cnbng_v6 cnbng
!
interface Bundle-Ether1.102 cnbng profile cnbng_v6
Access Interface Configuration
We define and associate access interface to cnBNG. This way control packets (based on configurations) get routed to the cnBNG CP. The contruct follows ASR9k Integarted BNG model, if you are familiar with.
interface Bundle-Ether1.102
ipv4 point-to-point
ipv4 unnumbered Loopback1
ipv6 enable
pppoe enable
encapsulation ambiguous dot1q 102 second-dot1q any
!
Note: This example uses ambiguous VLAN for access interface which allows 1:1 VLAN model. cnBNG also supports N:1 VLAN model for subscribers.
Radius Profile
Following are Freeradius profiles used in this tutorial. Profile-1 is for PPPoE PTA session and Profile-2 is for PPPoE LAC session.
Profile-1: PPPoE PTA
cisco Cleartext-Password:="cisco"
Framed-protocol += "PPP",
Service-Type += "Framed",
cisco-avpair += "subscriber:inacl=iACL_BNG_IPv4",
Cisco-AVpair += "subscriber:ipv6_inacl=iACL_BNG_IPv6",
cisco-avpair += "subscriber:sa=FT_Plan_100mbps",
cisco-avpair += "ip:primary-dns=200.45.191.45",
cisco-avpair += "ip:secondary-dns=8.8.8.8"
Profile-2: PPPoE LAC
cisco-lac Cleartext-Password:="cisco"
Framed-Protocol=PPP,
Service-Type=Outbound-User,
Tunnel-Type=L2TP,
Tunnel-Medium-Type=:1:IP,
Tunnel-Client-Endpoint=":1:<your-user-plane-loopback0-ip>",
Tunnel-Server-Endpoint=":1:<LNS IP>"
Verifications
- Verfiy that the cnBNG CP-UP association is up and Active on cnBNG CP ops-center
[cnbng-tme-lab/bng] bng# show peers | tab
Tue Jun 28 10:03:46.820 UTC+00:00
GR CONNECTED INTERFACE
INSTANCE ENDPOINT LOCAL ADDRESS PEER ADDRESS DIRECTION POD INSTANCE TYPE TIME RPC ADDITIONAL DETAILS NAME
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 RadiusServer - 192.168.107.152:1812 Outbound radius-ep-0 Udp 2 hours Radius Status: Active,Type: Auth <none>
0 RadiusServer - 192.168.107.152:1813 Outbound radius-ep-0 Udp 2 hours Radius Status: Active,Type: Acct <none>
1 n4 192.168.107.165:8805 192.168.107.142:8805 Inbound bng-nodemgr-0 Udp 2 hours UPF Name: ASR9k-1,Nm: 0/0,Status: ACTIVE <none>
- Verify that the CP-UP Association is Up and Active on cnBNG UP
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:ASR9k-1#show cnbng-nal cp connection status
Tue Jun 28 15:32:44.562 IST
Location: 0/RSP0/CPU0
User-Plane configurations:
-------------------------
IP : 192.168.107.142
GTP Port : 2152
PFCP Port : 8805
VRF : default
Control-Plane configurations:
----------------------------
PRIMARY IP : 192.168.107.165
GTP Port : 2152
PFCP Port : 8805
Association retry count: 5
Connection Status: Up
Connection Status time stamp: Tue Jun 28 13:10:16 2022
Connection Prev Status: Down
Connection Prev Status time stamp: Tue Jun 28 13:06:11 2022
Association status: Active
Association status time stamp: Tue Jun 28 13:10:15 2022
- Verify subscriber sessions are up on cnBNG CP ops-center
[cnbng-tme-lab/bng] bng# show subscriber session
Tue Jun 28 10:06:03.878 UTC+00:00
subscriber-details
{
"subResponses": [
{
"records": [
{
"cdl-keys": [
"16777229@sm",
"acct-sess-id:cnbng-tme-lab_DC_16777229@sm",
"upf:ASR9k-1",
"port-id:ASR9k-1/Bundle-Ether1.102",
"feat-template:pppoe-1",
"type:sessmgr",
"mac:0010.9401.0001",
"sesstype:lac",
"smupstate:smUpSessionCreated",
"up-subs-id:ASR9k-1/2148182752",
"smstate:established"
]
}
]
},
{
"records": [
{
"cdl-keys": [
"16777230@sm",
"acct-sess-id:cnbng-tme-lab_DC_16777230@sm",
"upf:ASR9k-1",
"port-id:ASR9k-1/Bundle-Ether1.102",
"feat-template:pppoe-1",
"type:sessmgr",
"mac:0010.9402.0001",
"sesstype:ppp",
"feat-template:FT_Plan_100mbps",
"smupstate:smUpSessionCreated",
"up-subs-id:ASR9k-1/2148182768",
"smstate:established",
"afi:dual"
]
}
]
}
]
}
- Verify that the subscriber session is up and working on cnBNG UP
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:ASR9k-1#show cnbng-nal subscriber all
Tue Jun 28 15:34:17.767 IST
Location: 0/RSP0/CPU0
Codes: CN - Connecting, CD - Connected, AC - Activated,
ID - Idle, DN - Disconnecting, IN - Initializing
CPID(hex) Interface State Mac Address Subscriber IP Addr / Prefix (Vrf) Ifhandle
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
100000d BE1.102.pppoe2148182752 AC 0010.9401.0001 200.200.210.1 (default) 0x2143e0
100000e BE1.102.pppoe2148182768 AC 0010.9402.0001 20.0.0.5 (default) 0x214420
2001::1 (IANA)
Session-count: 2
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:ASR9k-1#show subscriber running-config interface name BE1.102.pppoe2148182752
Tue Jun 28 15:34:58.796 IST
Building configuration...
!! IOS XR Configuration 7.4.2
subscriber-label 0x800aaae0
end
* Suffix indicates the configuration item can be added by aaa server only
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:ASR9k-1#show subscriber running-config interface name BE1.102.pppoe2148182768
Tue Jun 28 15:35:18.238 IST
Building configuration...
!! IOS XR Configuration 7.4.2
subscriber-label 0x800aaaf0
dynamic-template
type user-profile U000aaaf0
ipv6 access-group iACL_BNG_IPv6 ingress
ipv4 mtu 1500
ipv4 unnumbered Loopback1
ipv4 access-group iACL_BNG_IPv4 ingress
ipv6 enable
!
type service-profile FT_Plan_100mbps
service-policy input PM_Plan_100mbps_input
service-policy output PM_Plan_100mbps_output
!
!
end
Note: The ACL and QoS policies applied on subscriber interface must be defined on ASR9k (cnBNG UP), prior to subscriber session bring-up.
- Let’s now check l2tp tunnel status on cnBNG CP.
[cnbng-tme-lab/bng] bng# show l2tp-tunnel
Tue Jun 28 10:09:22.560 UTC+00:00
tunnel-details
{
"tunResponses": [
{
"records": [
{
"cdl-keys": [
"ASR9k-1:r:172.0.0.2:srcip:200.200.210.1:dstip::gid@l2tp",
"56084:tid:ASR9k-1:r@l2tp",
"type:l2tp-tunnel",
"upf:ASR9k-1",
"tunnel-id:56084",
"srcIP:172.0.0.2",
"dstIP:200.200.210.1",
"tunnel-type:lac",
"l2tp-profile:lac-1",
"state:complete"
]
}
]
}
]
}
Leave a Comment