Future of Multicast
IP Multicast Evolution
The purpose of the following blog is to give an insight on Business Multicast Service. We will explain how Multicast is currently deployed and how we propose to evolve these deployments in the future. Multicast is a technology used by many Service Providers (SP) but is very limited to Unicast in terms of deployments and evolution. Cisco currently has customers who are using different flavours of Multicast and it is expected to keep supporting all of them. However, we believe that Multicast should shift to new technology requirements and adapt to the upcoming evolution of IP Multicast.
Multicast in the SP world
SPs are split into 3 main categories:
- Media Streaming.
- Business Multicast VPN.
- Financial Streaming.
However, all of them have common Multicast goals such as:
- Deliver data to multiple locations.
- Optimize bandwidth utilisation by replicating data in the IP network.
- Assure the fair distribution of data across multiple sites (receivers, leaves) at the same time.
Our task here is to list these categories and propose solutions based on the current and future industry requirements.
Media Streaming
The Media Streaming customers are CNBC, Sky, BT Broadcast, Bell Broadcast, Verizon, Swisscom, Pixar, ESPN, Disney and more.
Streaming media is all about traffic delivered and consumed in a continuous stream from a source to the receivers. The main goal is to deliver IPTV broadcast channels to all the presence points while maintaning zero disruption of services.
The main requirements are:
- Data delivery for Broadcast TV in different formats such as SD, HD, 4K and 8K.
- Creation of multiple leaves that are controlled by the operator and are always on.
- Protection of the above by deploying Disjoing trees and Live-Live traffic.
Current Deployments
Today, most Media Streaming deployments are running RSVP-TE P2MP + mVPN. The Multicast tree is created manually for scenarios such as disjointness and Live-Live scenarios and there is not visualization. There is no real-time view of the tree as computation is distributed.
Today’s Cisco Suggestion
In Cisco, we believe that there are better ways to deliver Media Streaming. We can get rid of manual tree creation and maintenance by deploying the Tree-SID technology which is a controller based approach to build a tree either static or dynamic. It is a result of PCE + Tree-SID + mVPN where Tree-SID is a SR P2MP policy. Below you can find a list of sources for better understanding of Tree-SID.
Tree-SID Demo and Video
Media Streaming Future
The Industry is moving forward and it is our task to tag alone. The majority of traffic is Unicast, thus it is undeniable that it will grow faster than Multicast. The new NPU’s are designed and optimized to increase the forwarding performance and speed while achieving lower per packet cost. There is also lower power consumption and heat generation, therefore, these NPU’s are not Multicast designed. In Addition, replication is happening at Ingress NPU only and it is no longer splitted between Ingress and Egress. In summary we should expect similar replication performance on newer equipment compared to older without any large improvement anymore.
Cisco is currently working with the CNC (Crosswork Network Collector) and Crosswork Optimization Engine (COE) team to delivery the visualization of Tree-SID. This collaboration will provide the following advantages and features:
- Smart TV apps consuming Unicast traffic will replace setup boxes which will reduce Operating Expenditure (OPEX) for SPs.
- There can be Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) as elastic mechanism to scale up during large broadcast events such as sports evemts, political events, etc…
This is how COE Dashboard looks like in which we can see a whole topology of different trees. 
Business Multicast VPN
Customers
Since 2002 Cisco Systems® has been providing the solution of Multicast VPN (mVPN). It is simple to set up, highly scalable and has minimal administrative overhead. Providers can dynamically provide multicast support over MPLS networks. It allows for the transport of a customer’s IP Multicast traffic across a provider’s VPN backbone transparently, and it is integrated transparently with the Cisco IOS® Unicast MPLS VPN solution. It allows a service provider to offer multicast services to its VPN customers in addition to its current Unicast VPN offering.
The mVPN solution uses GRE with unique multicast distribution tree (MDT) forwarding to realize the true scalability of native IP Multicast in the core network. Cisco mVPN is based on the Multicast domain solution with the highest level of optimization built into the Cisco solution with the help of default MDT and data MDT scaling enhancements. mVPN introduces multicast routing information to the VPN routing and forwarding table (VRF), creating a Multicast VRF.
Current Deployments
Service providers are not looking into replacing MVPN service. SPs have lots of small mVPN trees and fewer large mVPN trees. mVPN traffic does not increase much while unicast bandwidth continues to double every 18-24 months.
Cisco will continue to support customers who have deployed Rosen mVPN (profile 0) and mLDP mVPN (profile 14).
Today’s Cisco Suggestion
Suggested solutions:
- If there is no need for TE by mVPN is needed:
- IR (Ingress Replication) + mVPN for small VPNs: In IR packets are replicated by Ingress PE and send unicast packets over the core to the destination PEs.
- mLDP + mVPN for large VPNs.
- IR and mLDP could be deployed together within the same network. It is transparent to the end-user and easy to switch from one to another.
- SR-MPLS Unicast is another solution
Business Multicast VPN Future
Majority of SP’s will continue to deploy Rosen mVPN or mLDP with Segment Routing Unicast but Ingress Replication and Tree-SID could optimize replication by delivering more controller services.
The transition to Ingress mVPN and Tree-SID mVPN will allow the optimization of mVPN deployment by reducing CapEX and OpEX. The replication flow will entirely change because the controller will be able to optimize traffic replication by selecting the replication nodes. Additionally, deployments such as P2MP RSVP-TE mVPN will shift to Tree-SID.
The following screenshot reflects to Business Multicast VPN Future 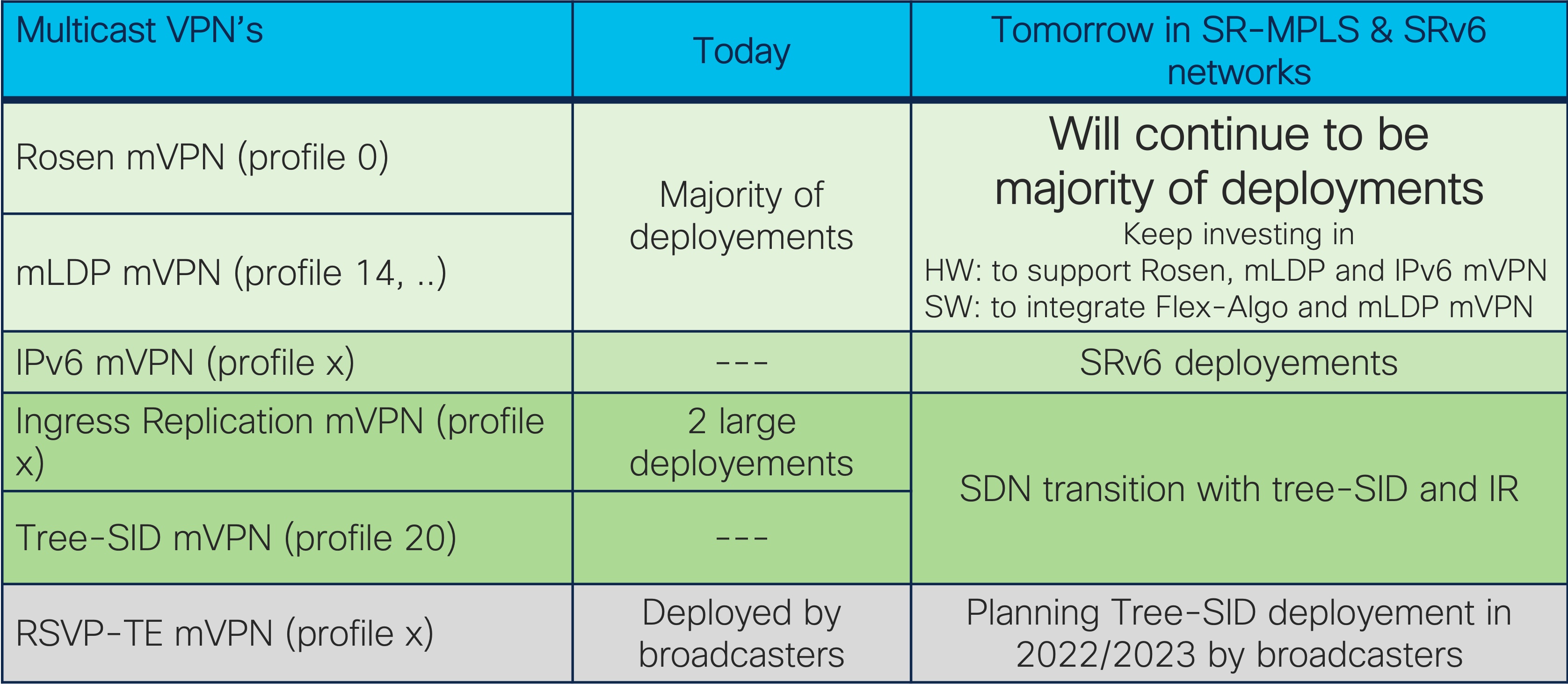
Financial Streaming
What broadcast SPs are saying (NBC, Sky, …): 1. They want to deploy disjoint live-live trees 2. Trees are fairly statics 3. Use to deploy RSVP-TE to address it -> the computation of disjoint trees is made manually and it is painful 4. Many are moving to Tree-SID + mVPN -> the computation of disjoing tree is automatic (thanks to SR-PCE) 5. COE (CrossWork Optimization Engine) and CNC (CrossWork Ip Network Controller) will add lots of value to the Tree-SID + mVPN solution, as the customer could now visualize 2 trees and prove their disjointness
What enterprise & financial are saying: 1. Wants to deploy disjoint live-live trees 2. Trees are dynamic and states are changing often 3. Looking at mLDP + FA + mVPN 4. Adding some constraint on topology and network design 5. Better suit for dynamic environment compared to Tree-SID
Current Deployments
Today’s Cisco Suggestion
Cisco would like to integrate Multicast with Unicast’s solutions such as Segment Routing, Flex-Algorithm (FA) and IPv6 transport.
- Need for TE in another working tree, computation with constraints (disjointness or other)
- mLDP + FA + mVPN: - Preferred solution when mVPNs are dynamic (lots of state changes)
- Limited to some topology (double plane design required, no ring topology)
- Tree-SID + mVPN: - Preferred solution when mVPNs are almost static
- Allow the customer to optimize multicast trees and simplify operation with a controller
- COE here ?
- mLDP + FA + mVPN: - Preferred solution when mVPNs are dynamic (lots of state changes)
Financial Streaming Future
IR SRv6 mVPN
Business Multicast VPN Future
_CDN strategy:
an example of SDN optimization for mVPN it is shown in this picture where the PCE controller’s role is to collect the topology. Collect information of what are the edge nodes with the source or leaf function and also compute what will be the optimal tree for that specific mVPN 06:05 and could select few nodes to be replication nodes, not all nodes are needed to be replication nodes_
Pragmatic use cases: Example of integrated Ingress replication and Tree-SID with SDN controller
The PCE (SDN controller) has the full visibility of the Multicast distribution and the topology.
Step 1: low number of lead and low bandwidth usage, the SDN controller could decide to limit this Tree-SID to Ingress Replication
Step 2: number of leaf augment or bandwidth increase, the SDN controller does select optimal replicators
add financial streaming (mldp +FA)
Non-TE solution (shortest path) » IR (Ingress Replication) + mVPN [IR over IPv6 unicast] » PIMv6 + mVPN TE based solution » PIMv6 + mVPN + FlexAlgo » Tree-SID (SRv6) + mVPN
Leave a Comment