LPTS Enhancements on NCS5500/NCS5700
Introduction
In our previous article, we had introduced the LPTS architecture on NCS5500 and NCS500 product family. There we discussed, concept of LPTS and its internal architecture. We also saw with examples how LPTS entries are created in the hardware and how they can be altered as per different requirements. We then followed it up with introduction to Domain based LPTS Policers and understanding its use cases. In this article, we will discuss the LPTS latest enhancements on the newer generation products.
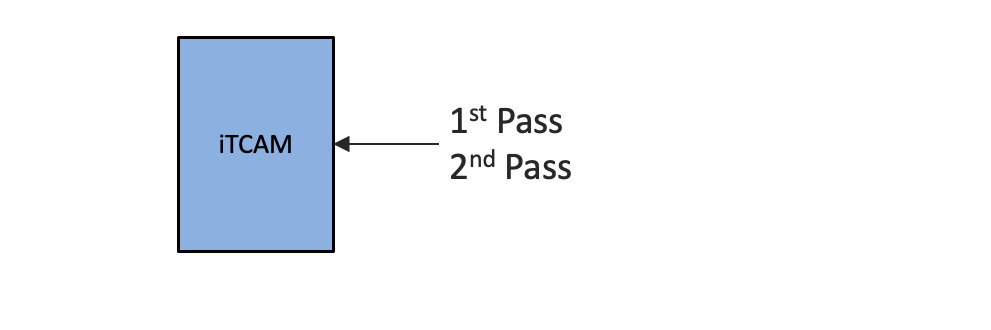
Brief Background
Before we move on to this topic, it would be recommended to visit our LPTS architecture document for understanding the implementation on the platform. As discussed in the document, LPTS is an integral component of IOS-XR systems which provides firewall and policing functionality. LPTS maintains per interface complete table in netio chain in Line card CPU, making sure that packets are delivered to their intended destinations. IOS XR software classifies all ‘For Us’ control packets into 97 different flows. Each flow has it own hardware policer to restrict the punt traffic rate for the flow type. We also discussed how the LPTS processes the for-us packets in the two pass in the hardware pipeline. For-us packets will go through the ASIC twice before getting punted to the CPU. In the current implementation this happens in iTCAM.
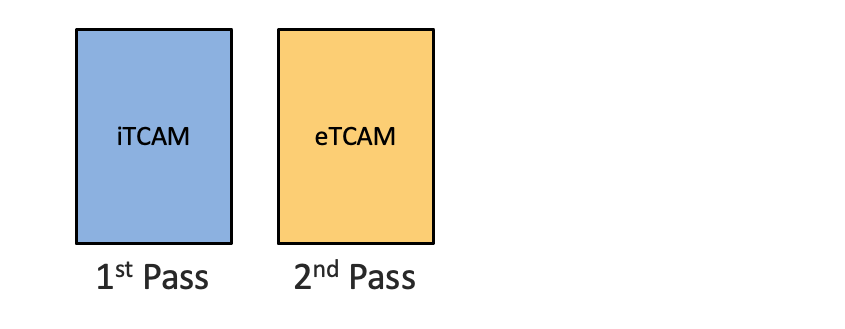
Problem Statement
Local Packet Transfer Services (LPTS) maintains tables that redirect packets to a logical router or the Secure Domain Router (SDR) to make sure that packets are delivered to their intended destination on the Routing Processor(RP). These packets are termed as “for-us” packets. Examples include PIM, IGMP, ICMP, RSVP other protocol packets like OSPFv2/v3 hello packets, ISIS packets, BGP packets etc. As mentioned above, the on chip TCAM or the iTCAM on previous generation NCS5500 can only support a maximum of 8K LPTS table entries along with other features. Entries exceeding the allowed numbers is processed under a common pool of software entries.
Solution
From IOS-XR 7.6.1, the scale of the LPTS hardware entries has been increased. To achieve the same, the second pass will happen in the eTCAM instead of iTCAM. This will help increase the LPTS hardware entries to 12000 (from current support of 8k). This helps in scaling the other protocol entries up to 1.5 times the current scale. This gives more flexibility to the customers to choose the number of hardware entries for their protocols.
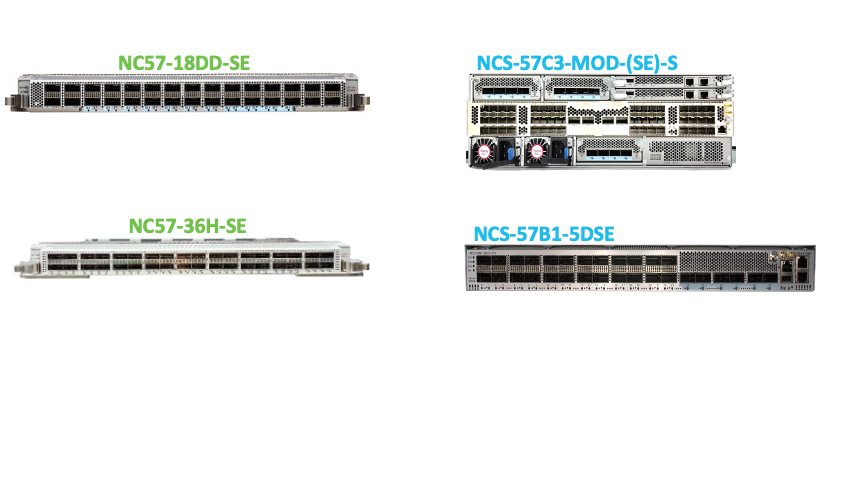
Platform Support
This enhancement is only supported on platforms based on Jericho2 and Jericho2C with external TCAM (NC57-18DD-SE, NC57-36H-SE, NCS-57C3-MOD-(SE)-S, NCS-57B1-5DSE). Platforms that do not have external TCAM does not support this enhancement. This is supported only in native mode. It is not supported in compatible mode. Earlier generation platforms based on Jericho/Jericho+ do not support this enhancement even if they have external TCAM.
For understanding Native vs Compatible mode please watch the following video.
Implementation
Let us have a high level understanding of how this works internally:
1st Pass
- The packet ingresses on the network interface and a forwarding destination lookup.
- This gives the packet a valid compression id value or a FEC value.
- Also the forwarding trap value for the packet may be set depending on the type of packet.
- In this stage, the trap value for the packet is modified to a user defined recycle trap id.
- This happens for packets that have a valid compression ID value.
- For packets with TTL=1, the TTL1 trap is set via INGRESS_IPV4/6 instead.
- Both traps ensures that the packet is recycled back to the IRPP.
2nd Pass
- The recycled packet lookup for 2nd pass happens in the external tcam is done via a recycle context selection criteria.
- This applies to all IPv4/v6 unicast and multicast packets and packets with the options attribute set.
- The hardware will have 2 lookups internally. The first will be for the forwarding destination or compression ID the other will be for LPTS.
Note: This happens transparently in the platforms once it is upgraded to IOS-XR 7.6.1 and operating in native mode
IOS-XR 7.6.1 Support Matrix
| Host Router | Remote Router | LPTS Scale |
|---|---|---|
| Platforms with J2/J2C with eTCAM Native Mode | Platforms with J2/J2C with eTCAM Native Mode | 12k |
| Platforms with J2/J2C with eTCAM Native Mode | Platforms with J2/J2C with eTCAM Compatible Mode | 8k |
| Platforms with J2/J2C with eTCAM Compatible Mode | Platforms with J2/J2C with eTCAM Native Mode | 8k |
| Platforms with J2/J2C without eTCAM Native/Compatible Mode | Platforms with J2/J2C without eTCAM Native/Compatible Mode | 8k |
| Platforms with J2/J2C without eTCAM Native/Compatible Mode | Platforms with J2/J2C with eTCAM Native/Compatible Mode | 8k |
| Platforms with J/J+ with eTCAM | Platforms with J/J+ with eTCAM | 8k |
| Platforms with J/J+ without eTCAM | Platforms with J/J+ without eTCAM | 8k |
| Platforms with J2/J2C with eTCAM Native/Compatible Mode | Platforms with J/J+ with eTCAM | 8k |
Configurations
Fixed platforms with J2/J2C ASIC with eTCAM will automatically support 12k LPTS entries when operating with IOS-XR 7.6.1.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:N57B1-1-Vega-II5-57#show platform
Node Type State Config state
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0/RP0/CPU0 NCS-57B1-5DSE-SYS(Active) IOS XR RUN NSHUT
0/PM0 PSU2KW-ACPI OFFLINE NSHUT
0/PM1 PSU2KW-ACPI OPERATIONAL NSHUT
0/FT0 N5700-FAN OPERATIONAL NSHUT
0/FT1 N5700-FAN OPERATIONAL NSHUT
0/FT2 N5700-FAN OPERATIONAL NSHUT
0/FT3 N5700-FAN OPERATIONAL NSHUT
0/FT4 N5700-FAN OPERATIONAL NSHUT
0/FT5 N5700-FAN OPERATIONAL NSHUT
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:N57B1-2-Vega-II5-58#show version
Mon Apr 11 09:17:51.091 UTC
Cisco IOS XR Software, Version 7.6.1 LNT
Copyright (c) 2013-2022 by Cisco Systems, Inc.
Build Information:
Built By : ingunawa
Built On : Sun Mar 27 01:23:01 UTC 2022
Build Host : iox-ucs-051
Workspace : /auto/srcarchive17/prod/7.6.1/ncs5700/ws
Version : 7.6.1
Label : 7.6.1
cisco NCS5700 (D-1563N @ 2.00GHz)
cisco NCS-57B1-5DSE-SYS (D-1563N @ 2.00GHz) processor with 32GB of memory
N57B1-2-Vega-II5-58 uptime is 3 hours, 6 minutes
NCS55B1 Fixed Scale HW Flexible Consumption Need Smart Lic
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:N57B1-2-Vega-II5-58#show lpts pifib dynamic-flows statistics location 0/RP0/CPU0
Dynamic-flows Statistics:
-------------------------
(C - Configurable, T - TRUE, F - FALSE, * - Configured)
Def_Max - Default Max Limit
Conf_Max - Configured Max Limit
HWCnt - Hardware Entries Count
ActLimit - Actual Max Limit
SWCnt - Software Entries Count
P, (+) - Pending Software Entries
FLOW-TYPE C Def_Max Conf_Max HWCnt/ActLimit SWCnt P
-------------------- -- ------- -------- -------/-------- ------- -
Fragment T 4 -- 2/4 2
OSPF-mc-known T 900 -- 0/900 0
OSPF-mc-default T 8 -- 4/8 4
OSPF-uc-known T 450 -- 0/450 0
OSPF-uc-default T 4 -- 2/4 2
ISIS-known T 300 -- 0/300 0
ISIS-default T 2 -- 1/2 1
BGP-known T 1800 -- 0/1800 0
BGP-cfg-peer T 1800 -- 0/1800 0
BGP-default T 8 -- 4/8 4
PIM-mcast-default T 40 -- 0/40 0
PIM-mcast-known T 450 -- 0/450 0
PIM-ucast T 40 -- 2/40 2
IGMP T 1464 -- 0/1464 0
ICMP-local T 4 -- 4/4 4
ICMP-control T 10 -- 5/10 5
ICMP-default T 18 -- 9/18 9
ICMP-app-default T 4 -- 2/4 2
LDP-TCP-known T 450 -- 0/450 0
LDP-TCP-cfg-peer T 450 -- 0/450 0
LDP-TCP-default T 40 -- 0/40 0
LDP-UDP T 450 -- 0/450 0
All-routers T 450 -- 0/450 0
RSVP-default T 4 -- 0/4 0
RSVP-known T 450 -- 0/450 0
IPSEC-known T 150 -- 0/150 0
SNMP T 150 -- 0/150 0
SSH-known T 150 -- 0/150 0
SSH-default T 40 -- 2/40 2
HTTP-known T 40 -- 0/40 0
HTTP-default T 40 -- 0/40 0
SHTTP-known T 40 -- 0/40 0
SHTTP-default T 40 -- 0/40 0
TELNET-known T 150 -- 0/150 0
TELNET-default T 4 -- 0/4 0
UDP-known T 40 -- 0/40 0
UDP-listen T 40 -- 0/40 0
UDP-default T 4 -- 2/4 2
TCP-known T 40 -- 0/40 0
TCP-listen T 40 -- 0/40 0
TCP-default T 4 -- 2/4 2
Raw-default T 4 -- 2/4 2
ip-sla T 50 -- 0/50 0
EIGRP T 40 -- 0/40 0
RIP T 40 -- 0/40 0
PCEP T 20 -- 0/20 0
GRE T 4 -- 0/4 0
VRRP T 150 -- 0/150 0
HSRP T 40 -- 0/40 0
MPLS-oam T 40 -- 0/40 0
DNS T 40 -- 0/40 0
RADIUS T 40 -- 0/40 0
TACACS T 40 -- 0/40 0
NTP-default T 4 -- 0/4 0
NTP-known T 150 -- 0/150 0
DHCPv4 T 40 -- 0/40 0
DHCPv6 T 40 -- 0/40 0
TPA T 100 -- 0/100 0
PM-TWAMP T 36 -- 0/36 0
---------------------------------------------------
Active TCAM Usage : 11450/12000 [Platform MAX: 12000]
HWCnt/SWCnt : 43/47
---------------------------------------------------
From the above output, we can see that when the router boots up with IOS-XR 761, we have only 11450 TCAM entries occupied. Whereas the maximum supported in 12000. This means that we have room to increase a particular flow without affecting the others. Let us check with an example.
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:N57B1-2-Vega-II5-58(config)#lpts pifib hardware dynamic-flows location 0/RP0/CPU0 flow bgp configured max 2000
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:N57B1-2-Vega-II5-58(config)#commit
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:N57B1-2-Vega-II5-58#show lpts pifib dynamic-flows statistics location 0/RP0/CPU0
Dynamic-flows Statistics:
-------------------------
(C - Configurable, T - TRUE, F - FALSE, * - Configured)
Def_Max - Default Max Limit
Conf_Max - Configured Max Limit
HWCnt - Hardware Entries Count
ActLimit - Actual Max Limit
SWCnt - Software Entries Count
P, (+) - Pending Software Entries
FLOW-TYPE C Def_Max Conf_Max HWCnt/ActLimit SWCnt P
-------------------- -- ------- -------- -------/-------- ------- -
Fragment T 4 -- 2/4 2
OSPF-mc-known T 900 -- 0/900 0
OSPF-mc-default T 8 -- 4/8 4
OSPF-uc-known T 450 -- 0/450 0
OSPF-uc-default T 4 -- 2/4 2
ISIS-known T 300 -- 0/300 0
ISIS-default T 2 -- 1/2 1
BGP-known T 1800 -- 0/1800 0
BGP-cfg-peer T* 1800 2000 0/2000 0
BGP-default T 8 -- 4/8 4
PIM-mcast-default T 40 -- 0/40 0
PIM-mcast-known T 450 -- 0/450 0
PIM-ucast T 40 -- 2/40 2
IGMP T 1464 -- 0/1464 0
ICMP-local T 4 -- 4/4 4
ICMP-control T 10 -- 5/10 5
ICMP-default T 18 -- 9/18 9
ICMP-app-default T 4 -- 2/4 2
LDP-TCP-known T 450 -- 0/450 0
LDP-TCP-cfg-peer T 450 -- 0/450 0
LDP-TCP-default T 40 -- 0/40 0
LDP-UDP T 450 -- 0/450 0
All-routers T 450 -- 0/450 0
RSVP-default T 4 -- 0/4 0
RSVP-known T 450 -- 0/450 0
IPSEC-known T 150 -- 0/150 0
SNMP T 150 -- 0/150 0
SSH-known T 150 -- 0/150 0
SSH-default T 40 -- 2/40 2
HTTP-known T 40 -- 0/40 0
HTTP-default T 40 -- 0/40 0
SHTTP-known T 40 -- 0/40 0
SHTTP-default T 40 -- 0/40 0
TELNET-known T 150 -- 0/150 0
TELNET-default T 4 -- 0/4 0
UDP-known T 40 -- 0/40 0
UDP-listen T 40 -- 0/40 0
UDP-default T 4 -- 2/4 2
TCP-known T 40 -- 0/40 0
TCP-listen T 40 -- 0/40 0
TCP-default T 4 -- 2/4 2
Raw-default T 4 -- 2/4 2
ip-sla T 50 -- 0/50 0
EIGRP T 40 -- 0/40 0
RIP T 40 -- 0/40 0
PCEP T 20 -- 0/20 0
GRE T 4 -- 0/4 0
VRRP T 150 -- 0/150 0
HSRP T 40 -- 0/40 0
MPLS-oam T 40 -- 0/40 0
DNS T 40 -- 0/40 0
RADIUS T 40 -- 0/40 0
TACACS T 40 -- 0/40 0
NTP-default T 4 -- 0/4 0
NTP-known T 150 -- 0/150 0
DHCPv4 T 40 -- 0/40 0
DHCPv6 T 40 -- 0/40 0
TPA T 100 -- 0/100 0
PM-TWAMP T 36 -- 0/36 0
---------------------------------------------------
Active TCAM Usage : 11650/12000 [Platform MAX: 12000]
HWCnt/SWCnt : 43/47
---------------------------------------------------
We can see that the hardware entries for BGP configured flow has been increased to 2000 from 1800. In the previous release this was not possible. All the 8k entries were utilised at the boot time itself. If we wanted to increase any particular flow, it would be at the cost of other flows.
For modular chassis we need to first bring the chassis to native mode using the below command. Then only this enhancement will be effective.
hw-module profile npu native-mode-enable
This will need a router reload. Once the chassis is operating in native mode and has line cards with external TCAM then we should be able to get the 12k LPTS entries.
If you want to toggle back to the previous behaviour for 8k entries then use the below profile and issue a router reload
hw-module profile tcam lpts-internal
Memory and Performance
Creating new field groups will take up hardware resources on the ASIC. But with the current implementation we will not face any memory issue. Though it uses 2 pass implementation but will not have any issues of latency in the platforms. This will be taken care at the boot time itself and will be transparent to the end users.
References
Introduction to LPTS on NCS5500 CCO Configuration Guide Short Video
Summary
LPTS provides a strong and compressive feature for control-plane protection. All the NCS5500 platforms are equipped with this feature, for helping the customers to achieve their SLAs and get better network stability. As discussed, this enhancement will help increase the LPTS scale and increase the number of hardware entries of the protocols along with other features. This will give flexibility to the customers in choosing hardware entries for the protocols. This is supported from IOS-XR 7.6.1 and only on the newer generation platforms with external TCAM. We have a roadmap to further increase this values from 12k. Stay tuned for the same.
Leave a Comment