How to find IOS-XR sensor-group from a CLI?
Introduction
I’ve been recently working on a Customer Proof of Concept where we demonstrated telemetry capabilities on ASR 9000, NCS 5500 and Cisco 8000 platforms. When going through the demo customer raised a good point: how do you find the telemetry sensor-group to configure? Is it intuition, a sixth sense?
This post will describe how to retrieve the YANG path for a given command and configure the corresponding sensor-group on an IOS-XR router.
CLI as telemetry starting point, really?
Let’s start with an actual example. We are interested in collecting information about L2VPN bridge-domain, and more specifically the number of unknown unicast packets received on an attachment circuit.
The first thing we do is to check the router CLI and find this information:
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:ASR9906_R1#sh l2vpn bridge-domain bd-name bd1 detail
Wed Mar 17 15:09:11.595 CET
Legend: pp = Partially Programmed.
Bridge group: bg1, bridge-domain: bd1, id: 8, state: up, ShgId: 0, MSTi: 0
Coupled state: disabled
VINE state: Default
MAC learning: enabled
MAC withdraw: enabled
MAC withdraw for Access PW: enabled
MAC withdraw sent on: bridge port up
MAC withdraw relaying (access to access): disabled
Flooding:
Broadcast & Multicast: enabled
Unknown unicast: enabled
MAC aging time: 300 s, Type: inactivity
MAC limit: 4000, Action: none, Notification: syslog
MAC limit reached: no, threshold: 75%
MAC port down flush: enabled
MAC Secure: disabled, Logging: disabled
Split Horizon Group: none
Dynamic ARP Inspection: disabled, Logging: disabled
IP Source Guard: disabled, Logging: disabled
DHCPv4 Snooping: disabled
DHCPv4 Snooping profile: none
IGMP Snooping: disabled
IGMP Snooping profile: none
MLD Snooping profile: none
Storm Control: disabled
Bridge MTU: 1500
MIB cvplsConfigIndex: 9
Filter MAC addresses:
P2MP PW: disabled
Multicast Source: Not Set
Create time: 16/03/2021 12:09:51 (1d02h ago)
No status change since creation
ACs: 1 (1 up), VFIs: 1, PWs: 2 (2 up), PBBs: 0 (0 up), VNIs: 0 (0 up)
List of ACs:
AC: HundredGigE0/2/0/4.20, state is up
Type VLAN; Num Ranges: 1
Rewrite Tags: []
VLAN ranges: [20, 20]
MTU 1500; XC ID 0x2000024; interworking none
MAC learning: enabled
Flooding:
Broadcast & Multicast: enabled
Unknown unicast: enabled
MAC aging time: 300 s, Type: inactivity
MAC limit: 4000, Action: none, Notification: syslog
MAC limit reached: no, threshold: 75%
MAC port down flush: enabled
MAC Secure: disabled, Logging: disabled
Split Horizon Group: none
E-Tree: Root
Dynamic ARP Inspection: disabled, Logging: disabled
IP Source Guard: disabled, Logging: disabled
DHCPv4 Snooping: disabled
DHCPv4 Snooping profile: none
IGMP Snooping: disabled
IGMP Snooping profile: none
MLD Snooping profile: none
Storm Control: bridge-domain policer
Static MAC addresses:
Statistics:
packets: received 80853079 (multicast 0, broadcast 0, unknown unicast 56120, unicast 80850611), sent 80795886
bytes: received 44145773679 (multicast 0, broadcast 0, unknown unicast 30445304, unicast 44144620123), sent 44114523280
MAC move: 0
Storm control drop counters:
packets: broadcast 0, multicast 0, unknown unicast 0
bytes: broadcast 0, multicast 0, unknown unicast 0
Dynamic ARP inspection drop counters:
packets: 0, bytes: 0
IP source guard drop counters:
packets: 0, bytes: 0
List of Access PWs:
List of VFIs:
VFI v1 (up)
--snip--
We can assume information is possibly present in some L2VPN YANG models. Let’s confirm it.
ANX to the rescue
Advanced NETCONF Explorer (ANX) is a tool written by Steven Barth at Cisco which has been open-sourced. ANX is great companion when it comes to explore telemetry and is very handy for this job.
After installing ANX and configuring netconf on your IOS-XR device, you can point ANX to the router:

ANX will retrieve and parse available YANG models:
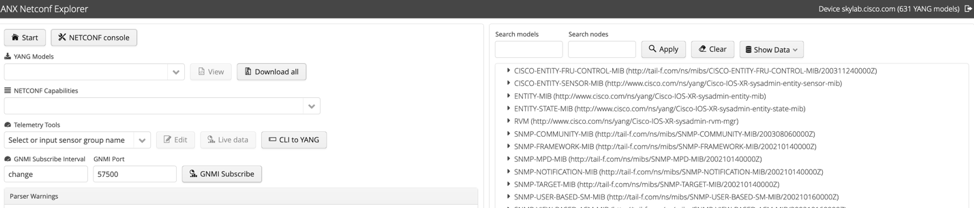
Number of available YANG models grows release after release. This can be verified on the GitHub repository. Make sure you use a recent IOS-XR version to benefit the latest ones and make the most of telemetry.
Once ANX has collected the models, they can be explored. If we take our L2VPN example, our instinct tells us to search into some L2PVN operational models, but there are a lot available:
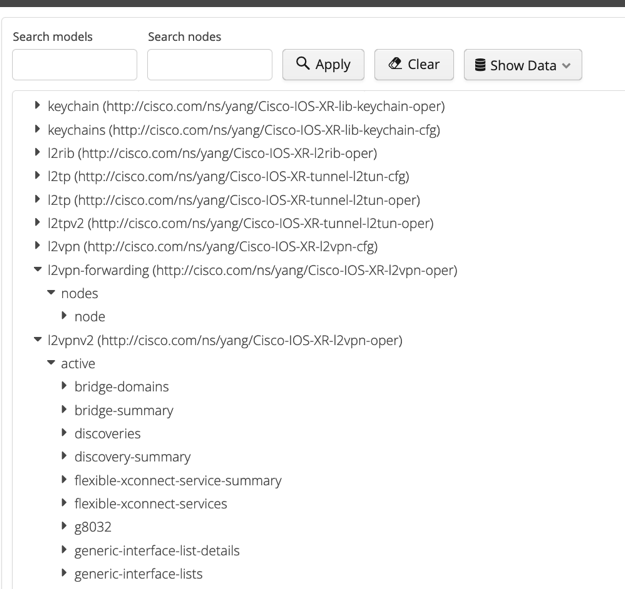
Search feature can be leveraged to perform additional filtering, but still too much information:
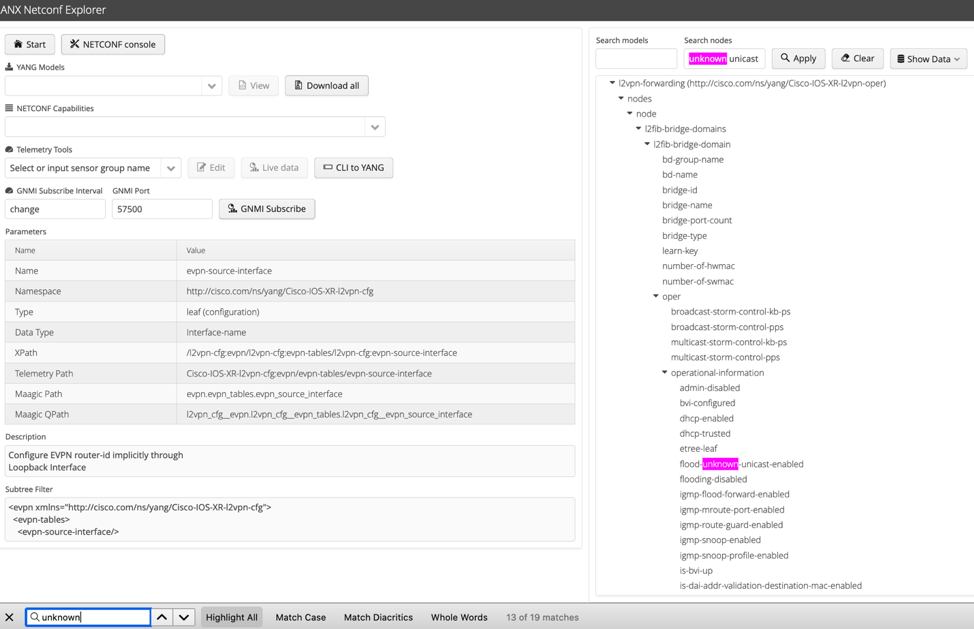
Good news is heavy lifting work can be offloaded to ANX with CLI to YANG feature. Enter a command, ANX will connect to the router and will try to discover the YANG schema:
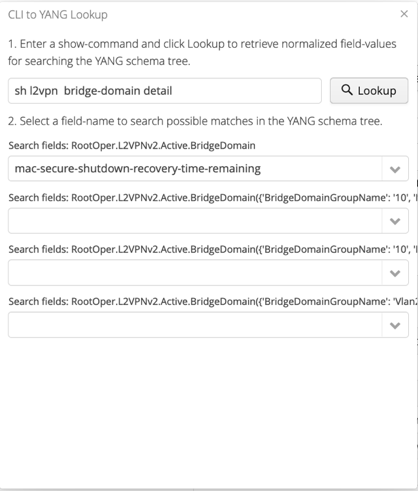
Finally, we find what we are looking for:
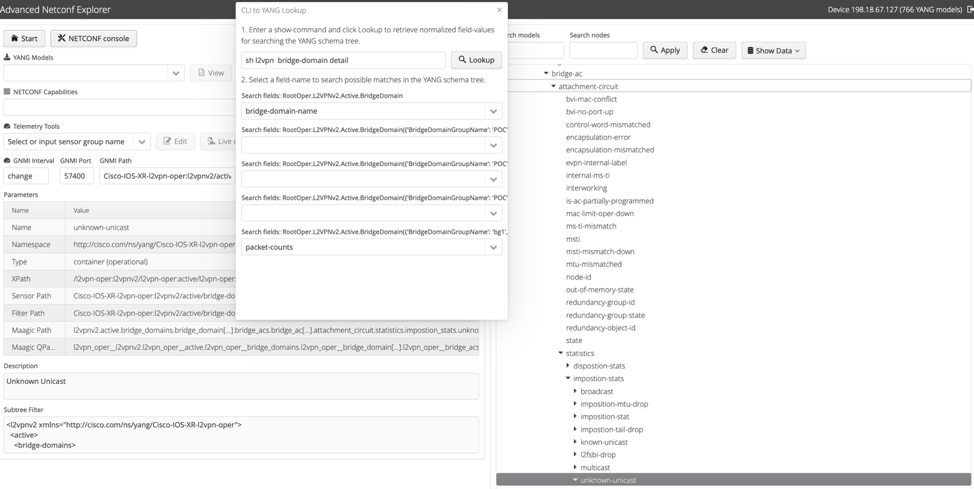
When clicking on the counter name, ANX displays the Sensor Path on the left:
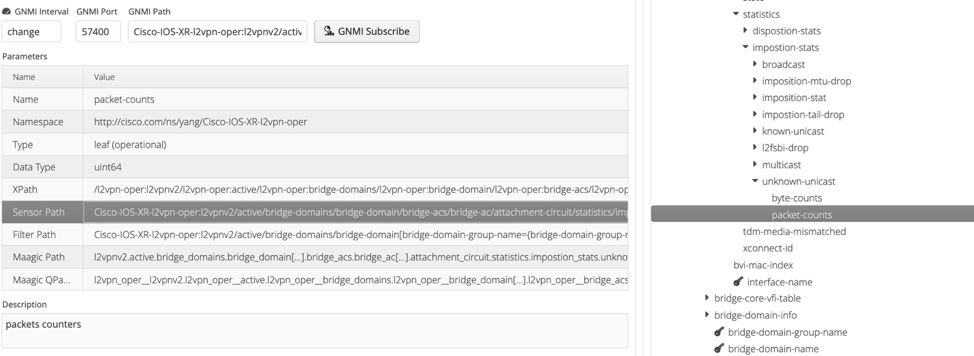
This is what needs to be configured on the router:
telemetry model-driven
sensor-group L2VPN-AC-COUNTERS
sensor-path Cisco-IOS-XR-l2vpn-oper:l2vpnv2/active/bridge-domains/bridge-domain/bridge-acs/bridge-ac/attachment-circuit/statistics/impostion-stats/unknown-unicast/packet-counts
Once sensor-group is configured, double check path is correctly resolved:
RP/0/RSP0/CPU0:ASR9906_R1#sh telemetry model-driven sensor-group L2VPN-AC-COUNTERS
Wed Mar 17 16:24:59.651 CET
Sensor Group Id:L2VPN-AC-COUNTERS
Sensor Path: Cisco-IOS-XR-l2vpn-oper:l2vpnv2/active/bridge-domains/bridge-domain/bridge-acs/bridge-ac/attachment-circuit/statistics/impostion-stats/unknown-unicast/packet-counts
Sensor Path State: Resolved
Router will start streaming counters after destination-group and subscription-group are configured like described in a previous post. Last, data can be explored and visualized with Grafana:
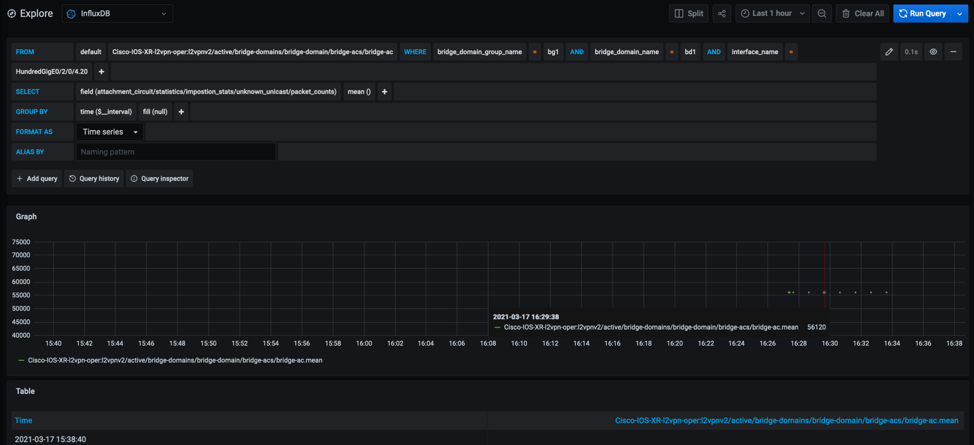
Et voilà.
What if I don’t have a router available?
ANX requires a connection to a device. If you don’t have hardware accessible, there are a couple of options available:
- Download and spin-up an IOS-XRv 9000 virtual machine on your infrastructure, pickup any version you want
- Use DevNet always-on sandbox. Current version is IOS-XRv 9000 6.5.3
Pay attention to Platform Dependent (PD) features and models: virtual routers might not have everything available (e.g low level NPU counters for a linecard, optics level).
Conclusion
This post covered how to retrieve and configure IOS-XR telemetry sensor-group using ANX. This simple example, starting with a show command, can be replicated for other counters you’d like to stream.
Leave a Comment