MPLS QoS on Cisco 8000 series routing platforms
Introduction
DiffServ Tunnelling Modes introduces a new Per-Hop-Behaviour (PHB), which allows differentiated QoS in a provider’s network. The tunnelling mode is defined at the edge of the network, normally in the PE Label Edge Router (LER) (both ingress and egress). You may need to make changes in the P routers; you must also consider what occurs when the topmost label is removed from a packet due to Penultimate-Hop-Popping (PHP). It may be necessary to copy the MPLS EXP value from the top label that is being popped to the newly exposed label; this does not always apply to all tunnelling modes.
This article explain on the MPLS QOS capabilities and implementation methods on Cisco 8000 series routing platforms.
Understanding PHP vs DiffServ
In some cases (for example, a plain non-VPN MPLS network), the PHP action on the final P router can expose a plain IP packet when a packet with only one label is received. When this IP packet is received by the egress LSR (PE), it is not possible to classify the packet based on the MPLS EXP bits because there is no label now. In these situations, you must configure the egress PE router to advertise an explicit-null label. When the PHP action is performed on the P router, a label with a value of zero is sent, and with this special label you can mark the EXP bits as normally labelled packets, allowing the correct classification on the egress PE router. The MPLS network support of DiffServ specification defines these tunnelling modes:
- Uniform
- Pipe
- Short-Pipe
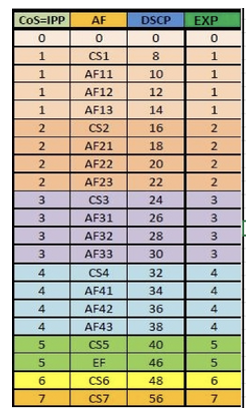
IP Precedence/DSCP to MPLS-EXP mapping
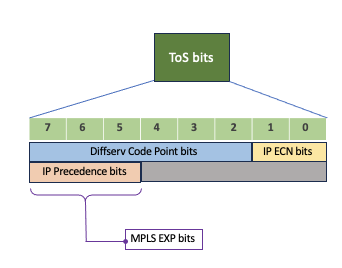
3 most significant bits (MSB) of IP ToS bits maps correspondingly to the MPLS-EXP bits. And same applied for L2 VLAN CoS bits to MPLS-EXP bits . And mapping for IP DSCP/Precedence values to MPLS EXP values are given below:
Default DiffServ transition behaviour in Cisco 8000 platforms
Below scenarios explains the default DiffServ marking behaviours in Cisco 8000 serues for packet paths like IP->MPLS, L2->MPLS, MPLS->MPLS, MPLS->IP and MPLS->L2 transitions without any marking policy applied on the device:
- MPLS-EXP is derived from the 3 MSBs of IP DSCP value in case of IPv4/IPv6 packet OR 3 bits of CoS value in case of VLAN tagged L2 packet while imposing label at the ingress PE node.
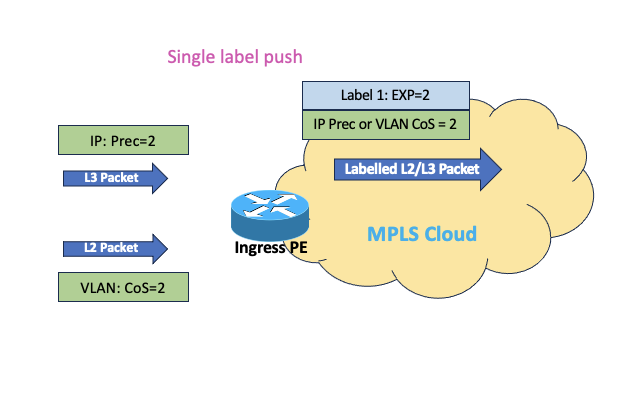
Note: If TCAM based (ACL) classification is applied at ingress on the ingress PE then MPLS EXP does not get derived from IP DSCP and it always gets zero. In such deployment, it’s required to have MPLS-EXP marking present in either ingress or egress policy.
- MPLS-EXP is derived from the 3 MSBs of IP DSCP value in case of IPv4/IPv6 packet OR 3 bits of CoS value in case of VLAN tagged L2 packet at ingress PE and this marking applies to all the labels which are getting pushed on the ingress PE node (both service and transport labels)
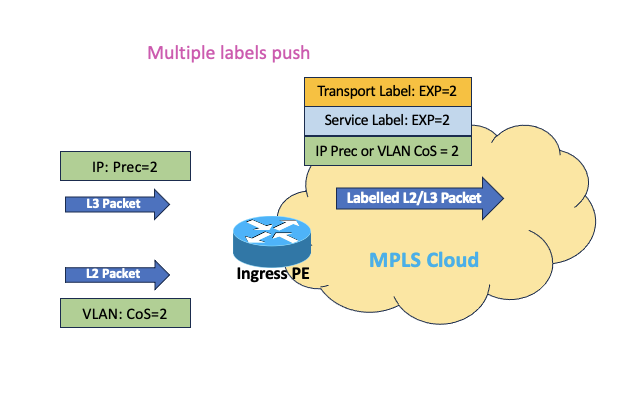
- And same applies to swap labels on P nodes
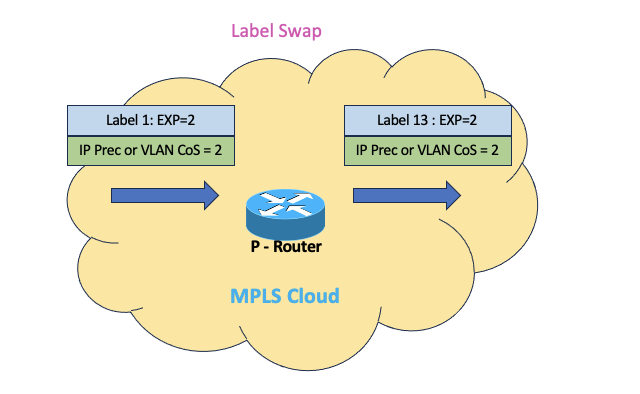
- Egress PE/PHP node does not copy EXP bits correspondingly to IP DSCP bits or CoS bits while popping labels and it just pop out the label without altering inner IP DSCP or L2 CoS bits.
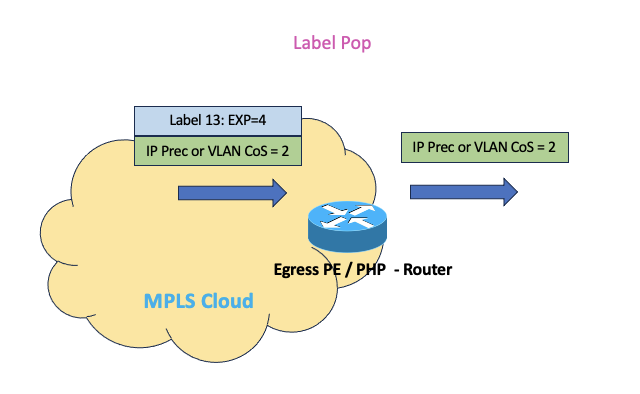
Understanding Uniform Mode
Uniform Mode is generally used when the customer and SP share the same DiffServ domain, as in the case of an enterprise deploying its own MPLS VPN core. In Uniform Mode, which is the default mode, the first 3 bits of the IP ToS field (IP Precedence bits) are automatically mapped to the MPLS EXP bits on the ingress PE as labels are pushed onto the packets. If policers or any other mechanisms remark the MPLS EXP values within the MPLS core, these marking changes are propagated to lower-level labels and eventually are propagated to the IP DSCP field. (MPLS EXP bits are mapped to IP DSCP values at the egress PE).
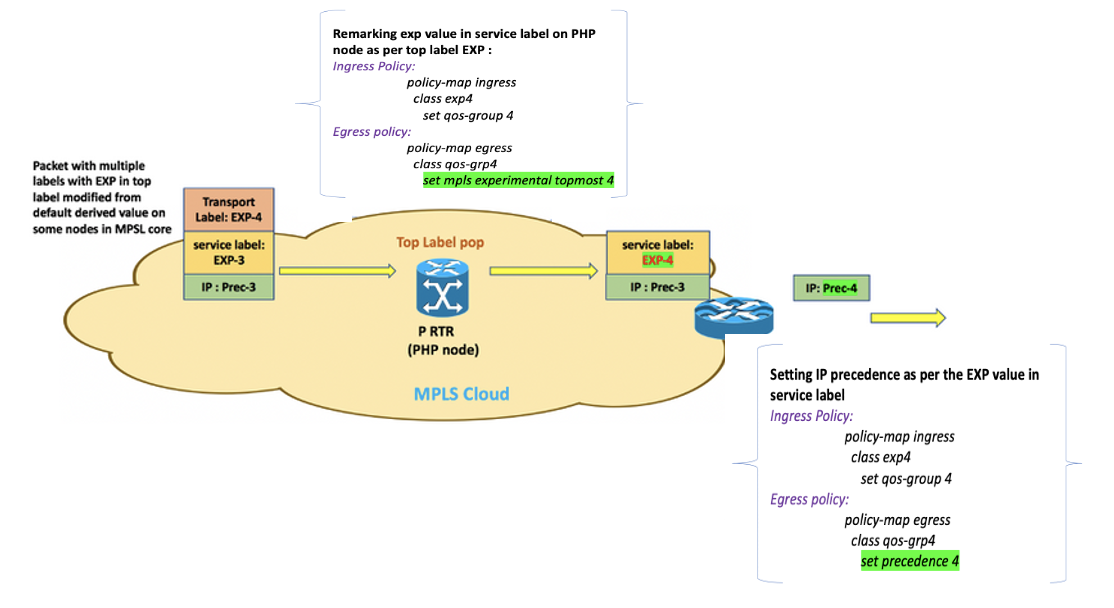
Uniform mode on Cisco 8000 with policy applications
If any remarking operation is executed within the MPLS core then remarked MPLS EXP in top label wont propagate to lower-level labels and corresponding bits to IP DSCP field. So below QoS operations are needed to achieve uniform mode on Cisco 8000:
Understanding Pipe Mode
DiffServ Tunneling Pipe Mode uses two layers of QoS:
- An underlying QoS for the data, which remains unchanged when traversing the core.
- A per-core QoS, which is separate from that of the underlying IP packets. This per-core QoS PHB remains transparent to end users.
- And EXPLICIT-NULL labelling is used here to provision the egress QoS based on provider’s DiffServ
Any changes to label markings occuring within the SP’s cloud do not get propagated to the IP DSCP field when the packet leaves the MPLS network. Pipe Mode differs from short-pipe mode in provisioning QoS at egress-PE node which is provisioned according to the SP’s explicit marking and remarking; not to customer’s IP DiffServ info although those are preserved.
Pipe mode on Cisco 8000 with policy application:
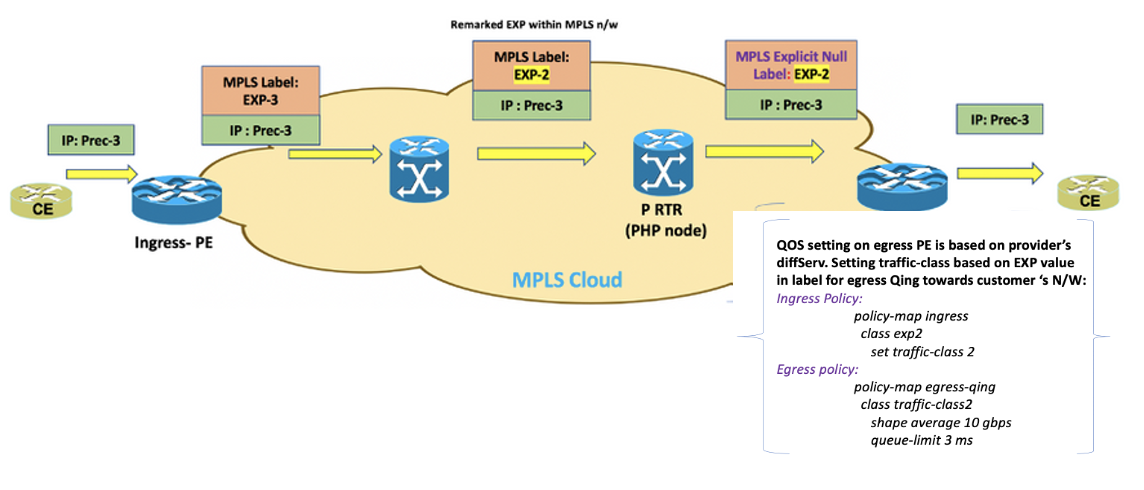
- Since provider is maintaining its own DiffServ , ingress remarking can be present at ingress PE if provider wants to serve based on different EXP values which are different from default derived value
- And egress QoS policy application achieves traffic treatment based on provider’s DiffServ on egress PE
IP -> MPLS Flow: Understanding Behavioural change in remarking IP DSCP/Prec & MPLS-EXP
There is an enhancement in remarking behaviour for IP to MPLS flows recently and the details are below,
Pre IOS XR 7.5.4/7.9.1 behaviour
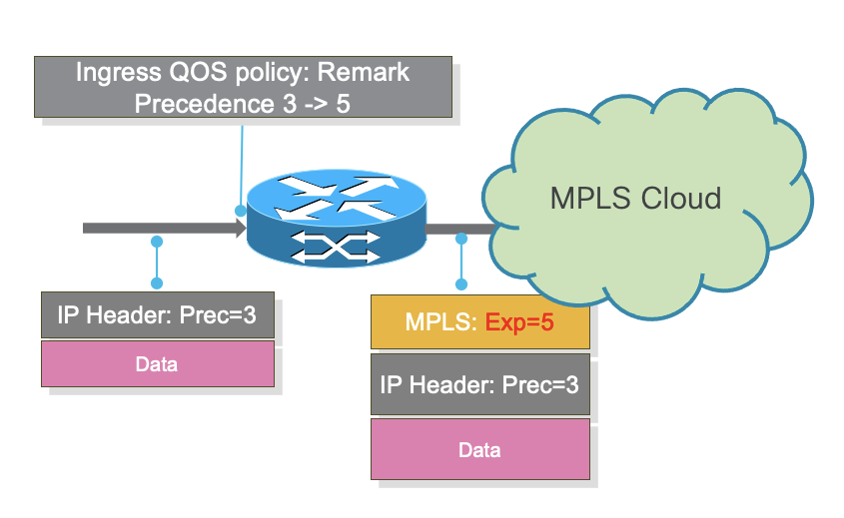
As seen in above picture, remarked precedence value is not reflected in outgoing packet. But at same time, MPLS-EXP value got derived from the remarked precedence value at ingress.
This behaviour is enhanced in IOS XR 7.5.4 and 7.9.1 releases and the behaviour is now the following: Outgoing labelled packet will have MPLS-EXP derived from the remarked precedence value and at same time remarked precedence value is updated in IP header of the outgoing packet
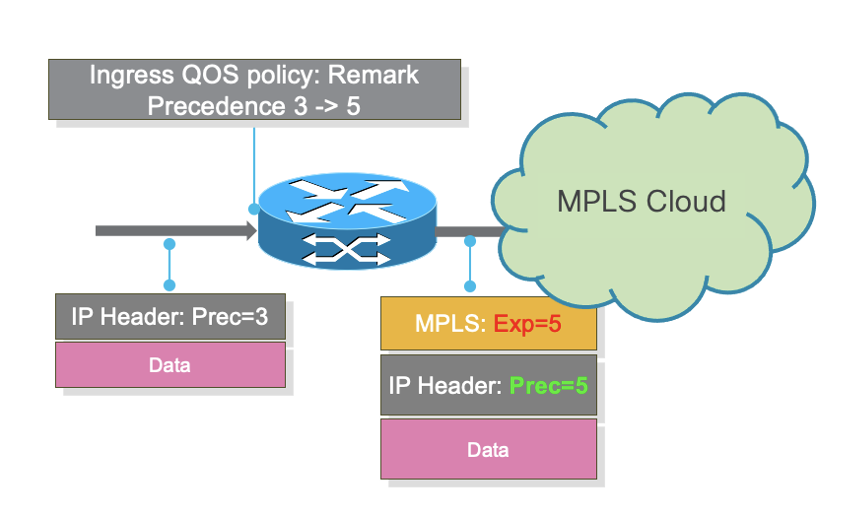
Notes :
- This feature is supported on Silicon One Q200 based device only, not on Q100.
- On Cisco 8800 distributed systems, ingress line card can be Q100 based but egress line card must be Q200 based as this feature capability is handled at egress NPU.
Conclusion
This article has briefed about the MPLS-QoS usecase and implementations on Cisco 8000 series routing devices specifically 8200/8600/8800 series platforms. Among different tunneling modes short-pipe is not completely addressed on Cisco 8000 where egress QOS is based on inner IP fields for labelled packets terminating on egress PE devices. And this capability will be considererd for new feature set.
Glossary
EXP : “Experimental” bits field on an MPLS header
Prec : “Precedence” bits field on an IPv4 header
DSCP : “Differentiated Service Code Point” bits field on an IPv4/IPv6 header
PE : Provider Edge PHP : Penultimate-Hop-Popping PHP : Per-Hop-Behaviour MSB : Most Significant Bit CoS : Class od Service
Leave a Comment