Managing OpenZR+ and OIF ZR transceivers on Cisco routers using OpenConfig
Revision History
| Version | Date | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 10/10/2022 | Initial Publication |
Routed Optical Networking
Routed Optical Networking introduced by Cisco in 2020 introduced a fundamental shift in how IP+Optical networks are built. Collapsing previously disparate network layers and services into a single unified domain, Routed Optical Networking simplifies operations and lowers overall network TCO. More information on Routed Optical Networking can be found at the following locations:
- https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/service-provider/routed-optical-networking.html
- https://xrdocs.io/latest-routed-optical-networking-hld
In this blog we will discuss one major component of Routed Optical Networking, the pluggable digital coherent optics, and how they are managed using open models from the OpenConfig consortium. Management includes both provisioning the transceivers as well as monitoring them via telemetry. OpenConfig support is found in IOS-XR 7.7.1 or later across all IOS-XR routers supporting ZR/ZR+ DCO transceivers. As you will see, the optical provisioning is distinct from the IP interface configuration and can be configured independently.
We will focus primarily on constructs such as OpenConfig YANG models and provisioning via NETCONF or gNMI. For users looking for a more UI-driven approach to managing Routed Optical Networking services, the Crosswork Hierarchical Controller application provides a point and click user interface, but still using open models to interface with Cisco routers. More information on the Crosswork family of products can be found at https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/cloud-systems-management/crosswork-network-automation/index.html
Pluggable Digital Coherent Optics
One of the foundations of Routed Optical Networking is the use of small form factor pluggable digital coherent optics. These optics can be used in a wide variety of network applications, reducing CapEx/OpEx cost and reducing complexity vs. using traditional external transponder equipment.
OIF 400ZR and OpenZR+ Standards using QSFP-DD Transceivers
The networking industry saw a point to improve network efficiency by shifting coherent DWDM functions to router pluggables. Technology advancements have shrunk the DCO components into the standard QSFP-DD form factor, meaning no specialized hardware and the ability to use the highest capacity routers available today. ZR/OpenZR+ QSFP-DD optics can be used in the same ports as the highest speed 400G non-DCO transceivers.
Cisco OpenZR+ Transceiver (QDD-400G-ZRP-S)
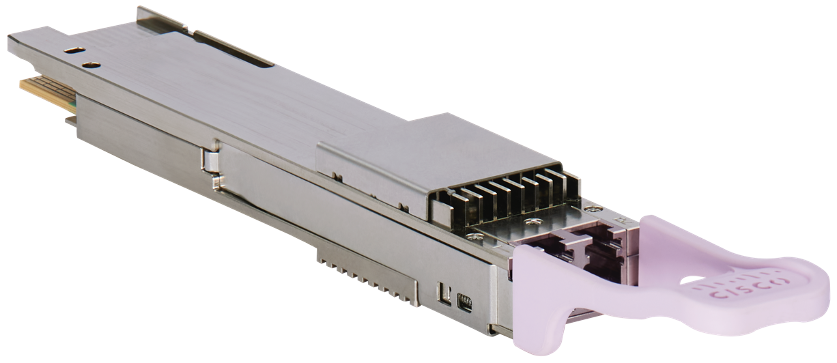
Cisco OIF 400ZR Transceiver (QDD-400G-ZR-S)
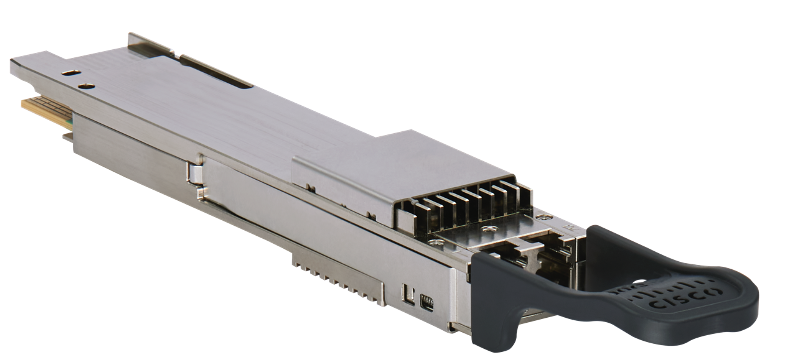
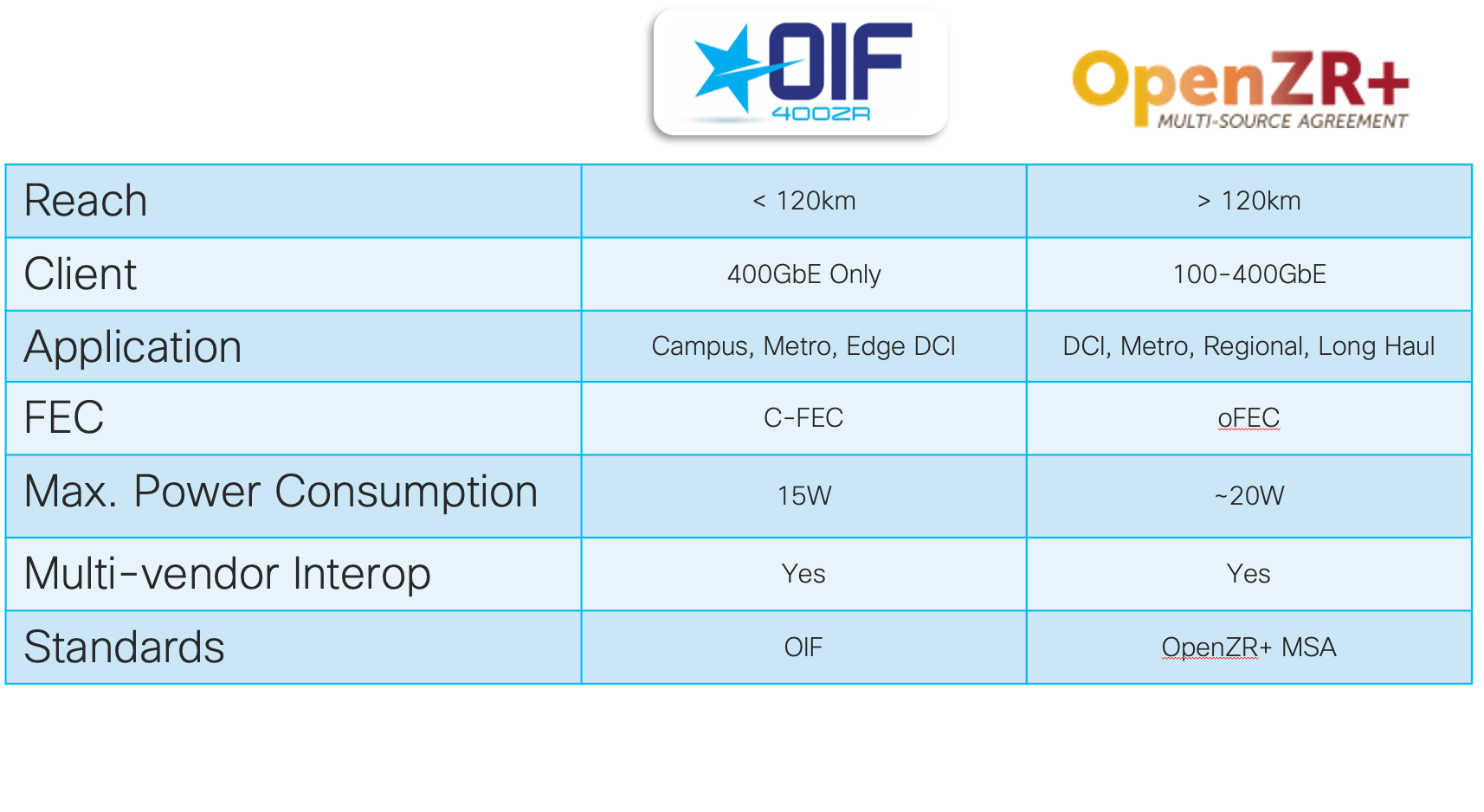
Two industry optical standards have emerged to cover a variety of use cases. The OIF created the 400ZR specification, https://www.oiforum.com/technical-work/hot-topics/400zr-2 as a 400G interopable standard for metro reach coherent optics. The industry saw the benefit of the approach, but wanted to cover longer distances and have flexibility in wavelength rates, so the OpenZR+ MSA was created, https://www.openzrplus.org. The following table outlines the specs of each standard. ZR400 and OpenZR+ transceivers are tunable across the ITU C-Band, 196.1 To 191.3 THz.
The following part numbers are used for Cisco’s ZR400 and OpenZR+ MSA transceivers
| Standard | Part |
|---|---|
| 400ZR | QDD-400G-ZR-S |
| OpenZR+ | QDD-400G-ZRP-S |
The Cisco datasheet for these transceivers can be found at https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/interfaces-modules/transceiver-modules/datasheet-c78-744377.html
Cisco Hardware Support for 400G ZR/ZR+ DCO Transceivers
Cisco supports the OpenZR+ and OIF ZR transceivers across all IOS-XR product lines with 400G QSFP-DD ports, including the ASR 9000, NCS 540, NCS 5500, NCS 5700, and Cisco 8000. Please see the Routed Optical Networking Design or the individual product pages below for more information on each platform.
Cisco 8000
NCS 500
Cisco ASR 9000
NCS 5500 and NCS 5700
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/routers/network-convergence-system-5500-series/datasheet-c78-736270.html
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/routers/network-convergence-system-5500-series/datasheet-c78-744698.html
Optical Provisioning Parameters
Optical transceivers are responsible for taking information on their electrical “host” interface and translating it into a format suitable for transmission across an analog medium, and vice versa. Thus the name “transceiver”. The aforementioned standards bodies have defined the electrical host interface and optical line interface specifications. The resulting configuration of those internal transceiver interfaces and parameters are driven by user configuration. The following represents the user-configurable attributes for Cisco ZR/ZR+ DCO transceivers.
| Parameter | Units | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Output Frequency | Hz | Frequency is another method to define the DWDM wavelength being used on the line side of the transceiver |
| Transmit Power | dBm | The transmit power defines the signal power level. dBm is the power ratio of dB referenced to 1mW using the expression dBm = 10log(mW). As an example 0dBm = 1mW, -3dBm=.50mW, +3dBM=2mW |
| Line Rate | Gbps | This is the output trunk rate of the signal, and may be determined by configuration or implicitly by the number of channels assigned |
| Operational Mode | Integer | The operational mode is an integer representing optical parameters specific to the transceiver. This includes settings such as the line rate, modulation, FEC type, and other vendor specific settings. |
The Frequency, Line Rate, and Operational Mode are required components. The Transmit Power is optional, a default power will be used based on the operational mode if none is supplied.
Operational Mode Details
It’s worth expanding on the role of the “Operational Mode” used in provisioning the transceivers. Cisco has defined a set of integer values used provision the QDD-400G-ZRP-S and QDD-400G-ZR-S optics based on standard parameters and Cisco Acacia specific parameters. The following table lists these modes.
| PID | Operational Mode | Line Rate | FEC Type | Modulation | Baud Rate | Pulse Shaping |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QDD-400G-ZR-S | 5003 | 400 | cFEC | 16QAM | 59.84 | No |
| QDD-400G-ZRP-S | 5004 | 400 | cFEC | 16QAM | 59.84 | No |
| QDD-400G-ZRP-S | 5005 | 400 | oFEC | 16QAM | 60.14 | Yes |
| QDD-400G-ZRP-S | 5006 | 400 | oFEC | 16QAM | 60.14 | No |
| QDD-400G-ZRP-S | 5007 | 300 | oFEC | 8QAM | 60.14 | Yes |
| QDD-400G-ZRP-S | 5008 | 300 | oFEC | 8QAM | 60.14 | No |
| QDD-400G-ZRP-S | 5009 | 200 | oFEC | QPSK | 60.14 | Yes |
| QDD-400G-ZRP-S | 5010 | 200 | oFEC | QPSK | 60.14 | No |
| QDD-400G-ZRP-S | 5011 | 200 | oFEC | 8QAM | 40.10 | Yes |
| QDD-400G-ZRP-S | 5012 | 200 | oFEC | 16QAM | 30.08 | Yes |
| QDD-400G-ZRP-S | 5013 | 100 | oFEC | QPSK | 30.08 | No |
OpenConfig
Taken from https://www.openconfig.net
OpenConfig defines and implements a common, vendor-independent software layer for managing network devices. OpenConfig operates as an open source project with contributions from network operators, equipment vendors, and the wider community. OpenConfig is led by an Operator Working Group consisting of network operators from multiple segments of the industry.
OpenConfig is advancing the paradigm of an abstract set of YANG models used to perform device configuration and monitoring regardless of vendor. Cisco has worked with the OpenConfig consortium since its inception to implement these open community models across IOS-XR, IOS-XE, and NX-OS devices. In IOS-XR 7.7.1 more than 100 OpenConfig models and sub-models are implemented covering a wide variety of network configuration including device management, routing protocols, and optical transceiver configuration. We will focus on the models specific to configuring the ZR/ZR+ DCO transceivers.
The official repository for all OpenConfig models can be found at https://github.com/openconfig/public/
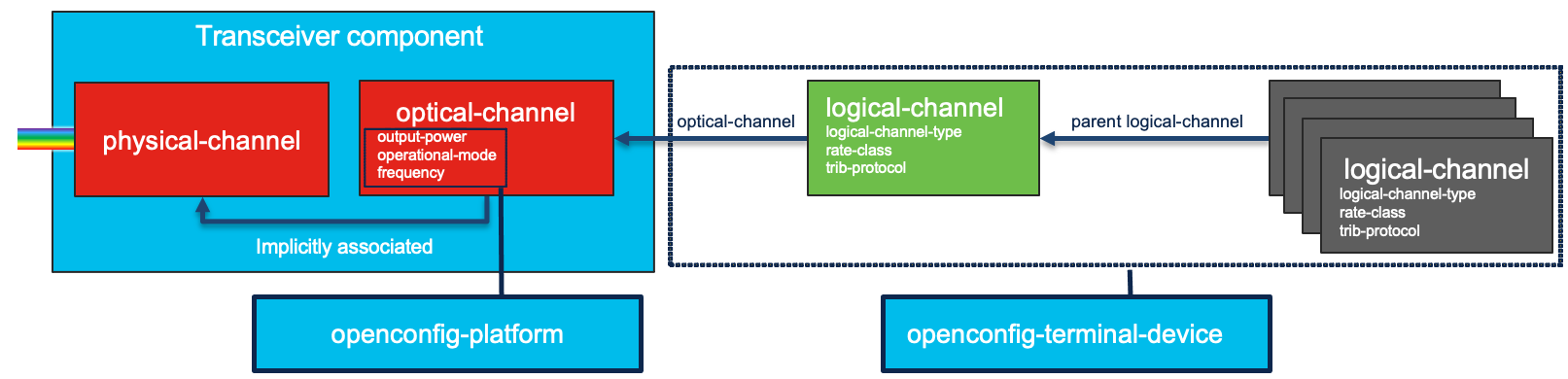
OpenConfig Models for DCO provisioning
This list is only the parent models utilized, and does include imported models.
| Model | Use |
|---|---|
| openconfig-terminal-device | Primary model used to configure input interface to output line port structure and add optical parameters to oc-platform |
| openconfig-platform | Used to provision optical channel parameters and for monitoring optical channel state |
| openconfig-platform-transceiver | Used for monitoring physical channel state data such as RX/TX power, and output frequency |
Note on Operational Mode Discovery
There is new work in OpenConfig to enable the discovery of the operational modes dynamically from the device/transceiver. As of this writing it’s still a relatively new concept and has not been implemented in IOS-XR. This is implemented through the openconfig-terminal-device-properties model. Once implemented a management application can learn the supported optical parameters and constraints to be used in path calculation and provisioning.
OpenConfig Platform Component
The optical parameters used to provision the parent optical-channel and subsequent physical channel are applied at the component level of the openconfig-platform model. The OpticalChannel component type is a logical component with a 1:1 correlation to a physical port. In Cisco routers The OpticalChannel component is populated when a transceiver capable of supporting it is inserted.
The OpticalChannel will always be represented as [Rack]/[Slot]-OpticalChannel[Rack][Slot][Instance][Port]. The rack component will always be 0. As an example on the 8201-32FH the OpticalChannel for port 20 is represented as 0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/20. On the NCS-57C3-MOD router with a QSFP-DD MPA in MPA slot 3 and DCO transceiver in Port 3 the OpticalChannel is 0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/3/2. On a Cisco 9904 modular router with a A9K-8HG-FLEX-TR line card in slot 1 and DCO transceiver in port 0, the OpticalChannel is 0/1-OpticalChannel-0/1/0/0.
Component Optical Provisioning Parameters
| Parameter | Units |
|---|---|
| frequency | Mhz |
| target-output-power | dBm to two decimal places expressed in increments of .01dBm (+1dBM=100) |
| operational-mode | Integer |
OpticalChannel Component Example
QDD-400G-ZRP-S in port 0/0/0/10 on Cisco 8201
<components xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/platform">
<component>
<name>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/10</name>
<config>
<name>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/10</name>
</config>
<optical-channel xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/terminal-device">
<config>
<target-output-power>-10.00</target-output-power>
<frequency>196100000</frequency>
<operational-mode>5005</operational-mode>
</config>
</optical-channel>
</component>
</components>
Openconfig Terminal Device
In the context of optical device provisioning, one OpenConfig model used is the Terminal Device model. The original intent of the model was to provision external optical transponders, and has been implemented by Cisco for use with the Cisco NCS 1004 muxponder. The model has been recently enhanced to cover the router pluggable DCO use cases where the “clients” are not physical external facing ports, but internal to the host router and always associated with a single external line facing interface. The Terminal Device model augments the Platform model to add the additional optical provisioning configuration parameters to the OpticalChannel component type.
Logical Channel Configuration
The logical channel has several configuration components, which will be the same across all similar configurations.
Each logical-channel created must be assigned an integer value. It is up to the user to determine the best overall values to use, but the values should not overlap between configuration on two different ports.
Traditional Muxponder Use Case
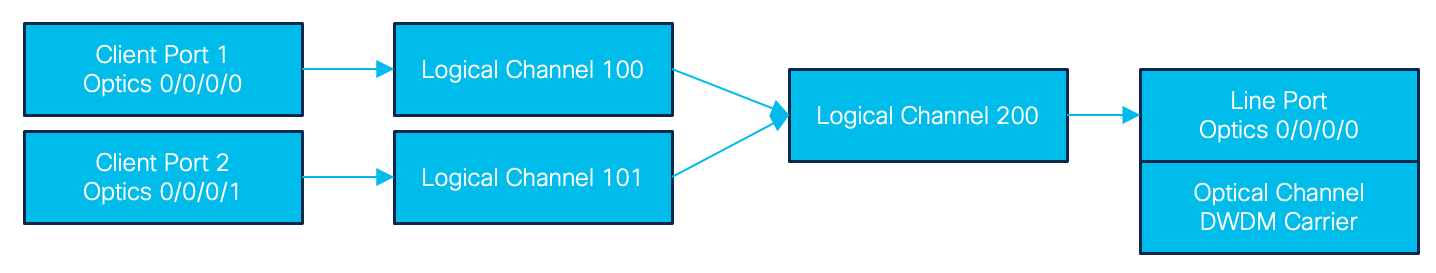
A traditional muxponder maps client physical interfaces to framed output timeslots, which can then be further aggregated or mapped to a physical output channel on the DWDM line side. There is no connection between the client port and line port until the mapping is created. The Terminal Device model follows this structure by using a hierarchical structure of channels from client to eventually output line port. Physical client channels are mapped to intermediate logical channels, which are ultimately mapped to a physical line output channel. The model is flexible based on the multiplexing/aggregation required.
The example below shows the mapping for a 2x100G muxponder application where the two client ports each map to a 100G logical channel, those map to a 200G logical channel, and ultimately to a 200G line port associated with the output optical channel. Note the numbers assigned to the logical channels are arbitrary integers.
Pluggable in Router Use Case
In the case where a pluggable coherent optic is inserted into a router, the hierarchical model can be simplified. In the traditional muxponder use case above, there is a physical client transceiver with its own properties which must be mapped into an intermediate logical channel. In the case of a router pluggable, there is no physical client component, only the logical components associated with the host side of the DCO transceiver. In Cisco routers, it is represented as one more Ethernet interfaces depending on the configuration.
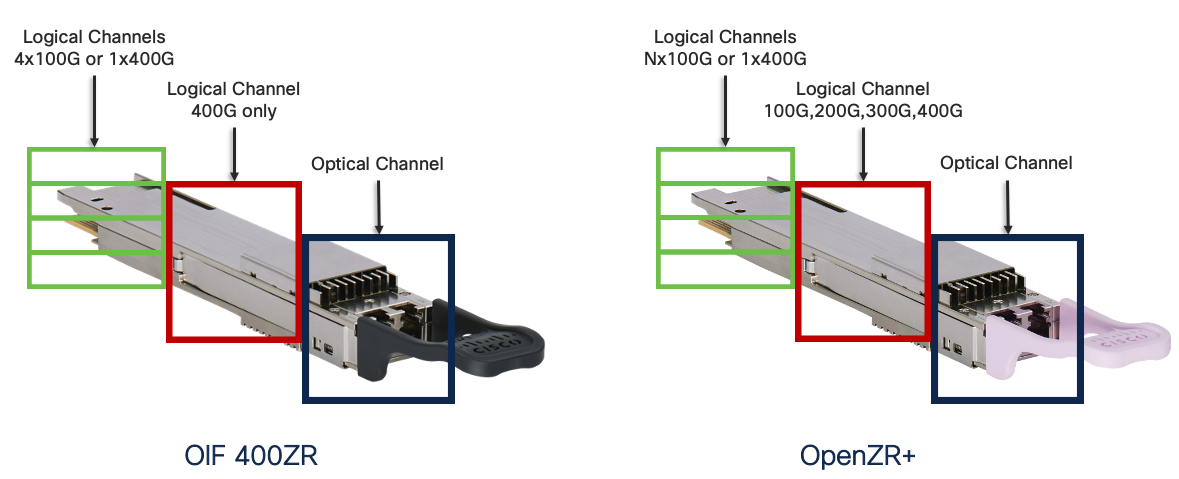
Looking at a picture of the two optics is helpful in showing how the hierarchical structure is configured for the DCO optics.
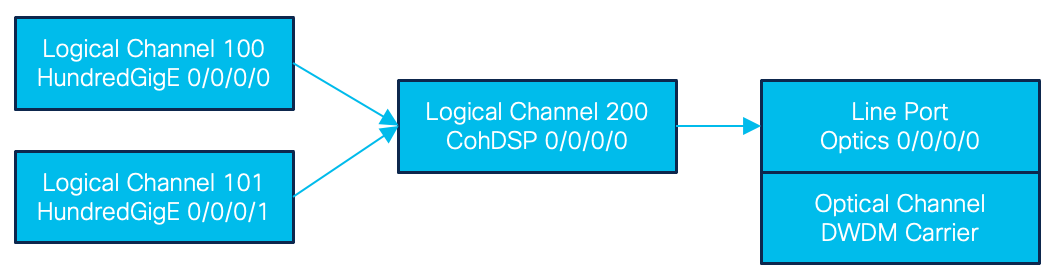
The example below shows a similar 200G application, but instead of two client physical ports, there are two HundredGigE interfaces created which are implicitly connected to the line port since they are integrated into the same transceiver. This is a fundamental difference from the muxponder use case where there is no implicit mapping between client and output port. The host side Ethernet interfaces of the DCO cannot be mapped to another line port.
Note this example is only possible with the OpenZR+ transceiver since it supports line rates of 100G, 200G, 300G, and 400G where the OIF 400ZR only supports 400G.
OpenConfig Provisioning Examples
The following examples are used to illustrate the complete provisioning payloads used. The payloads are given in XML for use with NETCONF, supported by all IOS-XR routers. We will go through two examples in detail and then the rest for the standard modes will provided in the appendix.
Standard OIF 400G ZR Example
OIF 400ZR transceivers, Cisco PID QDD-400G-ZR-S, can be configured in either 1x400G or 4x100G mode. In this example we will show the 1x400G mode, which is the most common configuration. The details of the configuration are:
| Router Type | Port Used | Operational Mode | Frequency | TX Power |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8201-32FH | 0/0/0/20 | 5003 | 194300000 | -100 |
Note the 5003 operational mode code which can be expanded as:
| PID | Rate | FEC | Modulation | Baud Rate | Pulse Shaping |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QDD-400G-ZR-S | 400G | cFEC | 16QAM | 60.14 | No |
<config>
<terminal-device xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/terminal-device">
<logical-channels>
<channel>
<index>100</index>
<config>
<index>100</index>
<rate-class xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:TRIB_RATE_400G</rate-class>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>ETH Logical Channel</description>
<trib-protocol xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_400GE</trib-protocol>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_ETHERNET</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>400</allocation>
<assignment-type>LOGICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>ETH to Coherent assignment</description>
<logical-channel>200</logical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
<channel>
<index>200</index>
<config>
<index>200</index>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>Coherent Logical Channel</description>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_OTN</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>400</allocation>
<assignment-type>OPTICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>Coherent to optical assignment</description>
<optical-channel>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/20</optical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
</logical-channels>
</terminal-device>
<components xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/platform">
<component>
<name>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/20</name>
<optical-channel xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/terminal-device">
<config>
<target-output-power>-100</target-output-power>
<operational-mode>5003</operational-mode>
<frequency>194300000</frequency>
</config>
</optical-channel>
</component>
</components>
</config>
Let’s examine some specific portions of the config in more detail.
<logical-channels>
<channel>
<index>100</index>
<config>
<index>100</index>
<rate-class xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:TRIB_RATE_400G</rate-class>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>ETH Logical Channel</description>
<trib-protocol xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_400GE</trib-protocol>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_ETHERNET</logical-channel-type>
</config>
Here we create the first logical channel, associated with the host Ethernet interface, FourHundredGigE0/0/0/20. Since our application has a single 400G interface, the following is configured. The types following the idx: YANG component are defined in openconfig-transport-types.yang.
| User-Defined Index | Tributary Rate Class | Tributary Protocol | Channel Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 400G | 400GE | ETHERNET |
Next we must map this logical-channel to either a parent logical-channel or output OpticalChannel. Cisco uses a specific “CoherentDSP” interface to represent the framing layer of the DCO transceiver, so there is a parent logical channel representing that layer of the connection. In this case I have a single 400G child interface, so all 400G is mapped to the parent logical channel.
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>400</allocation>
<assignment-type>LOGICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>ETH to Coherent assignment</description>
<logical-channel>200</logical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
Next we must define the parent logical-channel associated with the internal interface CoherentDSP0/0/0/20, and map that to the output OpticalChannel associated with the physical port. The rate is configured as 400 to represent 400G.
<channel>
<index>200</index>
<config>
<index>200</index>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>Coherent Logical Channel</description>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_OTN</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>400</allocation>
<assignment-type>OPTICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>Coherent to optical assignment</description>
<optical-channel>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/20</optical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
We will use the PROT_OTN encapsulation type for the channel, even though it’s not technically a traditional G.709 OTN frame.
| User-Defined Index | Channel Type |
|---|---|
| 200 | PROT_OTN |
This completes the configuration of the mappings between logical Ethernet and physical output port. Now we must configure the optical parameters using the openconfig-platform model.
<components xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/platform">
<component>
<name>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/20</name>
<optical-channel xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/terminal-device">
<config>
<target-output-power>-100</target-output-power>
<operational-mode>5003</operational-mode>
<frequency>194300000</frequency>
</config>
</optical-channel>
</component>
</components>
As you can see the configuration is relatively straightforward, applying the target-output-power, operational-mode, and frequency configuration.
300G Line Rate Configuration
When we configure ZR+ optics in a 300G line rate configuration, we must map individual 100G channels and Ethernet interfaces to a parent 300G container. There is no 300G Ethernet interface type defined, and based on how modern router NPUs are designed they are not typically well suited for creating intermediate containers of arbitrary size. The same is true of the 200G line rate as well.
Parameters of configuration are:
| Router Type | Port Used | Operational Mode | Frequency | TX Power |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8201-32FH | 0/0/0/20 | 5007 | 195200000 | Default |
Note the 5007 operational mode code which can be expanded as:
| PID | Rate | FEC | Modulation | Baud Rate | Pulse Shaping |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QDD-400G-ZRP-S | 300G | oFEC | 8QAM | 60.14 | Yes |
The full XML payload is:
<config>
<terminal-device xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/terminal-device">
<logical-channels>
<channel>
<index>100</index>
<config>
<index>200</index>
<rate-class xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:TRIB_RATE_100G</rate-class>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>ETH Logical Channel</description>
<trib-protocol xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_100G_MLG</trib-protocol>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_ETHERNET</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>100</allocation>
<assignment-type>LOGICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>ETH to Coherent assignment</description>
<logical-channel>200</logical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
<channel>
<index>101</index>
<config>
<index>101</index>
<rate-class xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:TRIB_RATE_100G</rate-class>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>ETH Logical Channel</description>
<trib-protocol xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_100G_MLG</trib-protocol>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_ETHERNET</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>100</allocation>
<assignment-type>LOGICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>ETH to Coherent assignment</description>
<logical-channel>200</logical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
<channel>
<index>102</index>
<config>
<index>102</index>
<rate-class xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:TRIB_RATE_100G</rate-class>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>ETH Logical Channel</description>
<trib-protocol xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_100G_MLG</trib-protocol>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_ETHERNET</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>100</allocation>
<assignment-type>LOGICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>ETH to Coherent assignment</description>
<logical-channel>200</logical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
<channel>
<index>200</index>
<config>
<index>200</index>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>Coherent Logical Channel</description>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_OTN</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>300</allocation>
<assignment-type>OPTICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>Coherent to optical assignment</description>
<optical-channel>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/20</optical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
</logical-channels>
</terminal-device>
<components xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/platform">
<component>
<name>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/20</name>
<optical-channel xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/terminal-device">
<config>
<operational-mode>5007</operational-mode>
<frequency>195200000</frequency>
</config>
</optical-channel>
</component>
</components>
</config>
First we will inspect the channel configuration for the child logical channel associated with the router Ethernet interface HundredGigE0/0/0/20/0. Inspecting the first one we see the following:
<channel>
<index>201</index>
<config>
<index>201</index>
<rate-class xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:TRIB_RATE_100G</rate-class>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>ETH Logical Channel</description>
<trib-protocol xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_100G_MLG</trib-protocol>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_ETHERNET</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>100</allocation>
<assignment-type>LOGICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>ETH to Coherent assignment</description>
<logical-channel>100</logical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
Here are the attributes used for the logical channel configuration:
| User-Defined Index | Tributary Rate Class | Tributary Protocol | Channel Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 100G | 100G_MLG | ETHERNET | |
| 101 | 100G | 100G_MLG | ETHERNET | |
| 102 | 100G | 100G_MLG | ETHERNET |
Note the Tributary Protocol type is now 100G_MLG. MLG stands for Multi-Link Group meaning this logical-channel is part of a larger MLG. The logical channel is still mapped to the upstream CoherentDSP0/0/0/20 logical-channel representing the channel responsible for multiplexing the child signals into a single output frame. Details on how this is done in OpenZR+ can be found in the OpenZR+ specifications at https://openzrplus.org. When IOS-XR receives the payload it will use the structured channel assignment information to properly allocate the child Ethernet interfaces.
The second logical channel associated with HundredGigE0/0/0/20/1 is similar with the only difference being the index of 101 instead of 100.
<channel>
<index>202</index>
<config>
<index>202</index>
<rate-class xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:TRIB_RATE_100G</rate-class>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>ETH Logical Channel</description>
<trib-protocol xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_100G_MLG</trib-protocol>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_ETHERNET</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>100</allocation>
<assignment-type>LOGICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>ETH to Coherent assignment</description>
<logical-channel>100</logical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
The Coherent DSP level logical-channel configuration is similar to the first example, except the allocation is now configured as 300 instead of 400 to reflect the 300G line rate.
<channel>
<index>100</index>
<config>
<index>100</index>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>Coherent Logical Channel</description>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_OTN</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>300</allocation>
<assignment-type>OPTICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>Coherent to optical assignment</description>
<optical-channel>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/20</optical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
The OpticalChannel configuration is also similar with the exception the target-output-power setting has been omitted. In this case the device default power of -1000 (-10dBM) will be used.
<components xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/platform">
<component>
<name>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/20</name>
<optical-channel xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/terminal-device">
<config>
<operational-mode>5007</operational-mode>
<frequency>195200000</frequency>
</config>
</optical-channel>
</component>
</components>
OpenConfig Monitoring Examples
The optics may also be monitored using the same OpenConfig models used for provisioning, as in OpenConfig models both config and state have leafs in the same model. We will look at two methods for retrieving operational state data, using a NETCONF GET and using GNMi which can be used in different ways to retrieve operational state data.
Using NETCONF
Optical Channel Information
Request from openconfig-platform for OpticalChannel 0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/8 associated with port 0/0/0/8.
<get xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0">
<filter>
<components xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/platform">
<component>
<name/>
<name>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/8</name>
</component>
</components>
</filter>
</get>
Response
<component>
<name>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/1</name>
<config>
<name>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/1</name>
</config>
<optical-channel xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/terminal-device">
<config>
<frequency>1600</frequency>
<target-output-power>0.00</target-output-power>
</config>
<state>
<target-output-power>0.00</target-output-power>
</state>
<extended xmlns="http://cisco.com/ns/yang/Cisco-IOS-XR-openconfig-terminal-device-ext">
<state>
<optics-cd-low-threshold>0</optics-cd-low-threshold>
<optics-cd-high-threshold>0</optics-cd-high-threshold>
</state>
</extended>
</optical-channel>
</component>
<component>
<name>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/8</name>
<config>
<name>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/8</name>
</config>
<optical-channel xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/terminal-device">
<config>
<target-output-power>-115</target-output-power>
<frequency>193700000</frequency>
<operational-mode>5005</operational-mode>
</config>
<state>
<target-output-power>-10.64</target-output-power>
<frequency>193700000</frequency>
<chromatic-dispersion>
<instant>-2</instant>
<interval>30000000000</interval>
<min>-4</min>
<avg>-2</avg>
<max>0</max>
<min-time>1664642812995785263</min-time>
<max-time>1664642792995781327</max-time>
</chromatic-dispersion>
<second-order-polarization-mode-dispersion>
<instant>37.00</instant>
<interval>30000000000</interval>
<min>35.00</min>
<avg>39.00</avg>
<max>42.00</max>
<min-time>1664642817995790775</min-time>
<max-time>1664642802995783064</max-time>
</second-order-polarization-mode-dispersion>
<polarization-dependent-loss>
<instant>1.10</instant>
<interval>30000000000</interval>
<min>1.10</min>
<avg>1.12</avg>
<max>1.20</max>
<min-time>1664642790996011456</min-time>
<max-time>1664642812995785263</max-time>
</polarization-dependent-loss>
<operational-mode>5005</operational-mode>
</state>
<extended xmlns="http://cisco.com/ns/yang/Cisco-IOS-XR-openconfig-terminal-device-ext">
<state>
<optics-cd-min>-13000</optics-cd-min>
<optics-cd-max>13000</optics-cd-max>
<optics-cd-low-threshold>-160000</optics-cd-low-threshold>
<optics-cd-high-threshold>160000</optics-cd-high-threshold>
</state>
</extended>
</optical-channel>
</component>
Physical Channel Information
Additional data from physical channel located as part of the openconfig-platform transceiver data. This is associated with the physical optics port referenced by 0/0-Optics0/0/0/8. ZR/ZR+ optics will always have a single physical channel.
Request
<get xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0">
<filter>
<components xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/platform">
<component>
<name/>
<name>0/0-Optics0/0/0/8</name>
</component>
</components>
</filter>
</get>
Response
<component>
<name>0/0-Optics0/0/0/8</name>
<transceiver xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/platform/transceiver">
<physical-channels>
<channel>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
</config>
<state>
<index>1</index>
<laser-bias-current>
<instant>65.67</instant>
<interval>30000000000</interval>
<min>0.07</min>
<avg>0.07</avg>
<max>0.07</max>
<min-time>1664642790996011456</min-time>
<max-time>1664642790996011456</max-time>
</laser-bias-current>
<output-power>
<instant>-10.64</instant>
<interval>30000000000</interval>
<min>-10.76</min>
<avg>-10.74</avg>
<max>-10.69</max>
<min-time>1664642790996011456</min-time>
<max-time>1664642817995790775</max-time>
</output-power>
<input-power>
<instant>-6.25</instant>
<interval>30000000000</interval>
<min>-6.34</min>
<avg>-6.27</avg>
<max>-6.21</max>
<min-time>1664642812995785263</min-time>
<max-time>1664642790996011456</max-time>
</input-power>
<output-frequency>193700000</output-frequency>
</state>
</channel>
</physical-channels>
<state>
<present>PRESENT</present>
<form-factor xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:OTHER</form-factor>
<date-code>2021-01-09T00:00:00Z+00:00</date-code>
<vendor-rev>01</vendor-rev>
<serial-no>ACA2501003X</serial-no>
<vendor-part>DP04QSDD-E30-19E</vendor-part>
<vendor>CISCO-ACACIA</vendor>
<connector-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:LC_CONNECTOR</connector-type>
<otn-compliance-code xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:OTN_UNDEFINED</otn-compliance-code>
<sonet-sdh-compliance-code xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:SONET_UNDEFINED</sonet-sdh-compliance-code>
<fault-condition>false</fault-condition>
</state>
</transceiver>
</component>
Using gNMI
gNMI represents a modern method to manage configuration as well as retrieve state data. gNMI data can be retrieved using different methods including a single GET request or through a subscription. The subscription type can be of types ONCE, STREAM, or POLL. The subsequent mode of the stream can be be SAMPLE, ON_CHANGE, or TARGET_DEFINED. The subscription type and mode commonly used for continuous monitoring is STREAM and SAMPLE. SAMPLE also includes a period value specifying the interval at which the device sends data. Note since we are using the same models, the data will be identical to the NETCONF example.
We will utilize the gNMIc utility found at https://gnmic.kmrd.dev/ for gNMI examples.
gNMI GET for OpticalChannel Data
Request
gnmic -a 172.29.11.20:57733 -u admin -p password --insecure --timeout 1m --encoding JSON_IETF get --path 'openconfig-platform:components/component[name='0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/8']'
Response
[
{
"source": "172.29.11.20:57733",
"timestamp": 1664644343717885105,
"time": "2022-10-01T13:12:23.717885105-04:00",
"updates": [
{
"Path": "openconfig-platform:components/component[name=0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/8]",
"values": {
"components/component": {
"config": {
"name": "0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/8"
},
"openconfig-terminal-device:optical-channel": {
"Cisco-IOS-XR-openconfig-terminal-device-ext:extended": {
"state": {
"optics-cd-high-threshold": 160000,
"optics-cd-low-threshold": -160000,
"optics-cd-max": 13000,
"optics-cd-min": -13000
}
},
"config": {
"frequency": 193700000,
"operational-mode": 5005,
"target-output-power": "-115"
},
"state": {
"chromatic-dispersion": {
"avg": "-1",
"instant": "-2",
"interval": "30000000000",
"max": "0",
"max-time": "1664644292995782101",
"min": "-2",
"min-time": "1664644307995794039"
},
"frequency": 193700000,
"operational-mode": 5005,
"polarization-dependent-loss": {
"avg": "1.09",
"instant": "1.10",
"interval": "30000000000",
"max": "1.10",
"max-time": "1664644290995999741",
"min": "1.00",
"min-time": "1664644317995786022"
},
"second-order-polarization-mode-dispersion": {
"avg": "42.37",
"instant": "51.00",
"interval": "30000000000",
"max": "52.00",
"max-time": "1664644297995784225",
"min": "39.00",
"min-time": "1664644307995794039"
},
"target-output-power": "-10.75"
}
}
}
}
}
]
}
]
gNMI Subscription for OpticalChannel Data
gnmic -a 172.29.11.20:57733 -u cisco -p cisco --insecure --timeout 1h --encoding JSON_IETF subscribe --path 'openconfig-platform:components/component[name='0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/8']' --mode stream --stream-mode sample --sample-interval 30s
[
{
"source": "172.29.11.20:57733",
"subscription-name": "default-1664645644",
"timestamp": 1664645651219000000,
"time": "2022-10-01T13:34:11.219-04:00",
"prefix": "openconfig-platform:",
"updates": [
{
"Path": "openconfig-platform:components/component[name=0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/8]",
"values": {
"components/component": {
"config": {
"name": "0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/8"
},
"openconfig-terminal-device:optical-channel": {
"Cisco-IOS-XR-openconfig-terminal-device-ext:extended": {
"state": {
"optics-cd-high-threshold": 160000,
"optics-cd-low-threshold": -160000,
"optics-cd-max": 13000,
"optics-cd-min": -13000
}
},
"config": {
"frequency": 193700000,
"operational-mode": 5005,
"target-output-power": "-115"
},
"state": {
"chromatic-dispersion": {
"avg": "-1",
"instant": "-2",
"interval": "30000000000",
"max": "0",
"max-time": "1664644292995782101",
"min": "-2",
"min-time": "1664644307995794039"
},
"frequency": 193700000,
"operational-mode": 5005,
"polarization-dependent-loss": {
"avg": "1.09",
"instant": "1.10",
"interval": "30000000000",
"max": "1.10",
"max-time": "1664644290995999741",
"min": "1.00",
"min-time": "1664644317995786022"
},
"second-order-polarization-mode-dispersion": {
"avg": "42.37",
"instant": "51.00",
"interval": "30000000000",
"max": "52.00",
"max-time": "1664644297995784225",
"min": "39.00",
"min-time": "1664644307995794039"
},
"target-output-power": "-10.75"
}
}
}
}
}
]
}
]
Appendix
Example XML NETCONF config for other ZR+ configuration modes
ZR+ 1x400G 16QAM
<config>
<terminal-device xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/terminal-device">
<logical-channels>
<channel>
<index>30001</index>
<config>
<index>30001</index>
<rate-class xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:TRIB_RATE_400G</rate-class>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>ETH Logical Channel</description>
<trib-protocol xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_400GE</trib-protocol>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_ETHERNET</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>400</allocation>
<assignment-type>LOGICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>ETH to Coherent assignment</description>
<logical-channel>30000</logical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
<channel>
<index>30000</index>
<config>
<index>30000</index>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>Coherent Logical Channel</description>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_OTN</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>400</allocation>
<assignment-type>OPTICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>Coherent to optical assignment</description>
<optical-channel>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/20</optical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
</logical-channels>
</terminal-device>
<components xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/platform">
<component>
<name>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/20</name>
<optical-channel xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/terminal-device">
<config>
<target-output-power>-115</target-output-power>
<operational-mode>5005</operational-mode>
<frequency>194300000</frequency>
</config>
</optical-channel>
</component>
</components>
</config>
ZR+ 1x100G QPSK
<config>
<terminal-device xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/terminal-device">
<logical-channels>
<channel>
<index>30001</index>
<config>
<index>30001</index>
<rate-class xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:TRIB_RATE_100G</rate-class>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>ETH Logical Channel</description>
<trib-protocol xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_100G_MLG</trib-protocol>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_ETHERNET</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>100</allocation>
<assignment-type>LOGICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>ETH to Coherent assignment</description>
<logical-channel>30000</logical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
<channel>
<index>30000</index>
<config>
<index>30000</index>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>Coherent Logical Channel</description>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_OTN</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>100</allocation>
<assignment-type>OPTICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>Coherent to optical assignment</description>
<optical-channel>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/20</optical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
</logical-channels>
</terminal-device>
<components xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/platform">
<component>
<name>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/20</name>
<optical-channel xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/terminal-device">
<config>
<target-output-power>-115</target-output-power>
<operational-mode>5013</operational-mode>
</config>
</optical-channel>
</component>
</components>
</config>
ZR+ 2x100G QPSK
<config>
<terminal-device xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/terminal-device">
<logical-channels>
<channel>
<index>30012</index>
<config>
<index>30012</index>
<rate-class xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:TRIB_RATE_100G</rate-class>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>ETH Logical Channel</description>
<trib-protocol xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_100G_MLG</trib-protocol>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_ETHERNET</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>100</allocation>
<assignment-type>LOGICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>ETH to Coherent assignment</description>
<logical-channel>30010</logical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
<channel>
<index>30013</index>
<config>
<index>30013</index>
<rate-class xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:TRIB_RATE_100G</rate-class>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>ETH Logical Channel</description>
<trib-protocol xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_100G_MLG</trib-protocol>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_ETHERNET</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>100</allocation>
<assignment-type>LOGICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>ETH to Coherent assignment</description>
<logical-channel>30010</logical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
<channel>
<index>30010</index>
<config>
<index>30010</index>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>Coherent Logical Channel</description>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_OTN</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>200</allocation>
<assignment-type>OPTICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>Coherent to optical assignment</description>
<optical-channel>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/20</optical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
</logical-channels>
</terminal-device>
<components xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/platform">
<component>
<name>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/20</name>
<optical-channel xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/terminal-device">
<config>
<target-output-power>-100</target-output-power>
<operational-mode>5009</operational-mode>
<frequency>191300000</frequency>
</config>
</optical-channel>
</component>
</components>
</config>
ZR+ 4x100G 16QAM
This mode does not have widespread applicability in routing applications but is included for completeness.
<config>
<terminal-device xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/terminal-device">
<logical-channels>
<channel>
<index>30009</index>
<config>
<index>30009</index>
<rate-class xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:TRIB_RATE_100G</rate-class>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>ETH Logical Channel</description>
<trib-protocol xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_100G_MLG</trib-protocol>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_ETHERNET</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>100</allocation>
<assignment-type>LOGICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>ETH to Coherent assignment</description>
<logical-channel>30013</logical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
<channel>
<index>30010</index>
<config>
<index>30010</index>
<rate-class xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:TRIB_RATE_100G</rate-class>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>ETH Logical Channel</description>
<trib-protocol xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_100G_MLG</trib-protocol>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_ETHERNET</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>100</allocation>
<assignment-type>LOGICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>ETH to Coherent assignment</description>
<logical-channel>30013</logical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
<channel>
<index>30011</index>
<config>
<index>30011</index>
<rate-class xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:TRIB_RATE_100G</rate-class>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>ETH Logical Channel</description>
<trib-protocol xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_100G_MLG</trib-protocol>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_ETHERNET</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>100</allocation>
<assignment-type>LOGICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>ETH to Coherent assignment</description>
<logical-channel>30013</logical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
<channel>
<index>30012</index>
<config>
<index>30012</index>
<rate-class xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:TRIB_RATE_100G</rate-class>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>ETH Logical Channel</description>
<trib-protocol xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_100G_MLG</trib-protocol>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_ETHERNET</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>100</allocation>
<assignment-type>LOGICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>ETH to Coherent assignment</description>
<logical-channel>30013</logical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
<channel>
<index>30013</index>
<config>
<index>30013</index>
<admin-state>ENABLED</admin-state>
<description>Coherent Logical Channel</description>
<logical-channel-type xmlns:idx="http://openconfig.net/yang/transport-types">idx:PROT_OTN</logical-channel-type>
</config>
<logical-channel-assignments>
<assignment>
<index>1</index>
<config>
<index>1</index>
<allocation>400</allocation>
<assignment-type>OPTICAL_CHANNEL</assignment-type>
<description>Coherent to optical assignment</description>
<optical-channel>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/20</optical-channel>
</config>
</assignment>
</logical-channel-assignments>
</channel>
</logical-channels>
</terminal-device>
<components xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/platform">
<component>
<name>0/0-OpticalChannel0/0/0/20</name>
<optical-channel xmlns="http://openconfig.net/yang/terminal-device">
<config>
<target-output-power>-115</target-output-power>
<operational-mode>5005</operational-mode>
<frequency>191300000</frequency>
</config>
</optical-channel>
</component>
</components>
</config>
Verification of OpenConfig in XR CLI
The IOS-XR CLI does contain configuration commands to either configure or verify OpenConfig configuration. The example below is for a 300G line rate application.
terminal-device
logical-channel 30000
admin-state enable
description Coherent Logical Channel
logical-channel-type Otn
assignment-id 1
allocation 300
assignment-type optical
description Coherent to optical assignment
assigned-optical-channel 0_0-OpticalChannel0_0_0_8
!
!
logical-channel 30001
rate-class 100G
admin-state enable
description ETH Logical Channel
trib-protocol 400GE
logical-channel-type Ethernet
assignment-id 1
allocation 400
assignment-type logical
description ETH to Coherent assignment
assigned-logical-channel 30000
!
!
logical-channel 30002
rate-class 100G
admin-state enable
description ETH Logical Channel
trib-protocol 100G-MLG
logical-channel-type Ethernet
assignment-id 1
allocation 100
assignment-type logical
description ETH to Coherent assignment
assigned-logical-channel 30000
!
!
logical-channel 30003
rate-class 100G
admin-state enable
description ETH Logical Channel
trib-protocol 100G-MLG
logical-channel-type Ethernet
assignment-id 1
allocation 100
assignment-type logical
description ETH to Coherent assignment
assigned-logical-channel 30000
!
!
optical-channel 0_0-OpticalChannel0_0_0_8
power -115
frequency 194300000
line-port Optics0/0/0/8
operational-mode 5007
!
!
IOS-XR CLI Operational Data
The main commands used to monitor optical information for the ZR/ZR+ optics is the show controller optics and show controller coherentdsp commands.
Example for QDD-400G-ZR-S
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ron-8201-1#show controllers optics 0/0/0/20
Thu Oct 6 14:31:25.413 PDT
Controller State: Down
Transport Admin State: In Service
Laser State: On
LED State: Yellow
FEC State: FEC ENABLED
Optics Status
Optics Type: QSFPDD 400G ZR
DWDM carrier Info: C BAND, MSA ITU Channel=61, Frequency=193.10THz,
Wavelength=1552.524nm
Alarm Status:
-------------
Detected Alarms: None
LOS/LOL/Fault Status:
Alarm Statistics:
-------------
HIGH-RX-PWR = 0 LOW-RX-PWR = 0
HIGH-TX-PWR = 0 LOW-TX-PWR = 5
HIGH-LBC = 0 HIGH-DGD = 0
OOR-CD = 0 OSNR = 9
WVL-OOL = 0 MEA = 0
IMPROPER-REM = 0
TX-POWER-PROV-MISMATCH = 0
Laser Bias Current = 52.5 mA
Actual TX Power = -10.06 dBm
RX Power = -40.00 dBm
RX Signal Power = -40.00 dBm
Frequency Offset = 0 MHz
Laser Temperature = 40.40 Celsius
Laser Age = 0 %
DAC Rate = 1x1
Performance Monitoring: Enable
THRESHOLD VALUES
----------------
Parameter High Alarm Low Alarm High Warning Low Warning
------------------------ ---------- --------- ------------ -----------
Rx Power Threshold(dBm) 13.0 -23.0 10.0 -21.0
Rx Power Threshold(mW) 19.9 0.0 10.0 0.0
Tx Power Threshold(dBm) 0.0 -18.0 -2.0 -16.0
Tx Power Threshold(mW) 1.0 0.0 0.6 0.0
LBC Threshold(mA) 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
Temp. Threshold(celsius) 80.00 -5.00 75.00 15.00
Voltage Threshold(volt) 3.46 3.13 3.43 3.16
LBC High Threshold = 98 %
Configured Tx Power = -10.00 dBm
Configured Tx Power(mW) = 0.10 mW
Configured CD High Threshold = 160000 ps/nm
Configured CD lower Threshold = -160000 ps/nm
Configured OSNR lower Threshold = 9.00 dB
Configured DGD Higher Threshold = 80.00 ps
Baud Rate = 59.8437500000 GBd
Modulation Type: 16QAM
Chromatic Dispersion 0 ps/nm
Configured CD-MIN -2400 ps/nm CD-MAX 2400 ps/nm
Second Order Polarization Mode Dispersion = 0.00 ps^2
Optical Signal to Noise Ratio = 0.00 dB
SNR = 0.00 dB
Polarization Dependent Loss = 0.00 dB
Polarization Change Rate = 0.00 rad/s
Differential Group Delay = 0.00 ps
Temperature = 42.00 Celsius
Voltage = 3.34 V
Transceiver Vendor Details
Form Factor : QSFP-DD
Optics type : QSFPDD 400G ZR
Name : CISCO-ACACIA
OUI Number : 7c.b2.5c
Part Number : DP04QSDD-E20-19E
Rev Number : 10
Serial Number : ACA245100ET
PID : QDD-400G-ZR-S
VID : ES03
Firmware Version : Major.Minor.Build
Active : 61.20.13
Inactive : 61.10.12
Date Code(yy/mm/dd) : 20/12/28
Fiber Connector Type: LC
Otn Application Code: Undefined
Sonet Application Code: Undefined
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ron-8201-1#show controllers coherentDSP 0/0/0/10
Thu Oct 6 14:31:55.222 PDT
Port : CoherentDSP 0/0/0/10
Controller State : Down
Inherited Secondary State : Normal
Configured Secondary State : Normal
Derived State : In Service
Loopback mode : None
BER Thresholds : SF = 1.0E-5 SD = 1.0E-7
Performance Monitoring : Enable
Bandwidth : 400.0Gb/s
Alarm Information:
LOS = 1 LOF = 0 LOM = 0
OOF = 0 OOM = 0 AIS = 0
IAE = 0 BIAE = 0 SF_BER = 0
SD_BER = 0 BDI = 0 TIM = 0
FECMISMATCH = 0 FEC-UNC = 0 FLEXO_GIDM = 0
FLEXO-MM = 0 FLEXO-LOM = 0 FLEXO-RDI = 0
FLEXO-LOF = 0
Detected Alarms : LOS
Bit Error Rate Information
PREFEC BER : 5.0E-01
POSTFEC BER : 0.0E+00
Q-Factor : 0.00 dB
Q-Margin : 0.00dB
OTU TTI Received
FEC mode : C_FEC
Leave a Comment