NCS-5700 400G Optics Technology and Roadmap
NCS-5700 400G Optics Technology and Roadmap
NCS-5700 is the first platform in the NCS-5500 Series that supports 400G optics, which is introduced in a previous tutorial:
Introducing 400GE on NCS5500 Series
This tutorial will discuss in more details the 400G optics technology and roadmap for the NCS-5700 series.
A follow up tutorial will discuss the 400G optics and breakout options supported for each port type on the NCS-5700 series linecards, NC57-24DD and NC57-18DD-SE.
Introducing QSFP-DD MSA
QSFP-DD is the leading form factor for 400G optics, promoted by QSFP-DD MSA. Members include Cisco and other major suppliers.
QSFP+ and QSFP28 are the de-facto standard for high density 40G and 100G optics.
QSFP-DD is fully compatible with QSFP+ and QSFP28, and so maintains the same port density.
The QSFP-DD MSA published its Revision 1.0 specifications in Sep 2016, and it is at its Revision 5.0 as of Jul 2019.

Number of Serdes
 QSFP-DD adds a second row of pins and increases the number of serdes from 4 to 8, hence the name double-density.
QSFP-DD adds a second row of pins and increases the number of serdes from 4 to 8, hence the name double-density.
It therefore supports optics up to 8 electrical lanes.
50G Serdes Support
QSFP-DD increases the maximum serdes speed from 25G to 50G, therefore supporting a maximum speed of 8x50G = 400G aggregate.
For backward compatibility, it also supports 10G and 25G serdes speed, thus allowing all possible aggregate speeds of 40G, 100G, 200G and 400G.
Optics of all form factors, such as QSFP+, QSFP28, QSFP56, QSFP28-DD and QSFP56-DD are supported by QSFP-DD.
PAM4 Encoding Support
QSFP-DD supports PAM4 encoding for 50G serdes, while maintaining the use of NRZ encoding for 10G/25G serdes.
PAM4 allows 2 bits per baud, so will double the serdes speed from 25G to 50G, while maintaining the same 25 GBaud rate.
RS-FEC RS(544,514) Support
QSFP-DD supports RS-FEC (Clause 91) RS(544,514) for 50G serdes, while maintaining the use of RS(528,514) for 25G serdes.
RS(528,514) is sometimes called the KR4 FEC, and RS(544,514) KP4 FEC.
RS(544,514) will provide a stronger FEC for use with higher speed serdes, and hence require a slightly higher overhead.
RS(528,514) is running at 25.78125 GBaud/s (25.78125 Gbit/s), and RS(544,514) is running at 26.5625 GBaud/s (53.125 Gbit/s)
High Power Support
QSFP-DD supports high power optics, therefore ready for coherent optics such as 400G-ZR and 400G-ZR+.
At OFC 2019, Cisco Demonstrate 20W+ power dissipation of QSFP-DD.
https://blogs.cisco.com/sp/cisco-demonstrates-20w-power-dissipation-of-qsfp-dd-at-ofc-2019
Flexible Breakout Support
The wide range of combination of serdes number and speeds provides very flexible breakout options:
| QSFP56-DD | QSFP28-DD | QSFP56 | QSFP28 | QSFP+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 400G | 200G | 200G | 100G | 40G |
| 2x200G | 2x100G | 2x100G | 4x25G | 4x10G |
| 4x100G | 8x25G | 4x50G | ||
| 8x50G |
400G Optics Technology Evolution
For early QSFP28 100G optics, majority are using 4x 25G wavelengths with NRZ encoding.
50G and 100G Wavelengths Evolution
With evolution to 200G/400G optics, there is a need for higher speed wavelengths in the optical domain, such as 50G/100G in order to reduce lasers cost and complexity.
25G wavelengths are supported using NRZ encoding with 25 GBaud and RS-FEC RS(528,514). 16x 25G wavelengths are required for an aggregate 400G speed.
50G wavelengths are supported using PAM4 encoding with 25 GBaud and RS-FEC RS(544,514). 8x 50G wavelengths are required for an aggregate 400G speed.
100G wavelengths are supported using PAM4 encoding with 50 GBaud and RS-FEC RS(544,514). An even lower number of wavelengths, 4x, are required for an aggregate 400G speed.
Distance and Fiber Types
Generally the 400G optics distance support will be dependent on the type of cables or fibers used.
For very short distances up to a few meters, usually copper cables or active optical cables will be most cost effective.
For short distances up to about 100m, usually multimode fibers (MMF) with 850nm wavelength are deployed for lower cost. Furthermore, parallel fibers, each with single wavelength, are used to reduce optics complexity.
For medium distances to about 500m, usually parallel single mode fibers (SMF) with 1310nm wavelength are deployed.
For longer distances 2km and beyond, usually a single duplex SMF fiber pair is deployed with 1310nm wavelengths to minimize fiber numbers and cost. Multiple wavelengths are multiplexed into a single SMF using WDM technologies, such as CWDM or LWDM. LWDM is higher cost and usually for longer distances.
To reach even longer distances like 80km and above, usually Coherent Detection optics with 1550nm wavelength are used, which have their own specific encoding and FEC, and have single tunable wavelength at speed 100G or 400G. These wavelengths may even be transported over long haul DWDM systems and reach 1000’s of km’s.
Bidirectional Optics Support
Bidirectional optics can save half the number of fibers, as each fiber supports 2 wavelengths, one in each direction.
For example, 400GBase-SR8 requires 8 pairs of MMF, total 16 fibers. Each fiber supports one wavelength in one direction, total 16 wavelengths.
In case of bidirectional 400GBase-SR4.2, it only requires 4 pairs of MMF, total 8 fibers. Each fiber run 2 wavelengths, one in each direction, total also 16 wavelengths.
WDM technology is required for the multiplexing, such as SWDM in the case of 400GBase-SR4.2 and 100G-SWDM2.
Parallel Fiber and Breakout Support
Generally, parallel fibers have additional advantage of supporting breakout from 400G to multiple lower speed optics for more flexible deployment.
Any types of parallel cables, MMF or SMF can support breakout, and usually each piece of fiber will support one wavelength.
For example, 400GBase-DR4 have 4 MMF fibers, each with one 100G wavelength, therefore it could support 4x100G breakout.
Timeline for 400G Optics Standards Development
This is a brief summary of the latest optics standards with 50G, 100G or 400G wavelengths.
Most optics standards are from IEEE 802.3 Ethernet Standards Committee.
However, in some areas, various MSA standards will also provide important supplement to the IEEE standards, and we have included some of them below.
| Date | Specs | Standard | Speed | W/L | Distance | Cable | Freq | Type | Breakout | WDM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 Dec | IEEE 802.3bs | 400GBase-SR16 | 400G | 25G | 100m | MMF OM4 | 850nm | Parallel | Y | |
| 400GBase-DR4 | 400G | 100G | 500m | SMF | 1310nm | Parallel | Y | |||
| 400GBase-FR8 | 400G | 50G | 2km | SMF | 1310nm | Duplex | N | LWDM | ||
| 400GBase-LR8 | 400G | 50G | 10km | SMF | 1310nm | Duplex | N | LWDM | ||
| 200GBase-DR4 | 200G | 50G | 500m | SMF | 1310nm | Parallel | Y | |||
| 200GBase-FR4 | 200G | 50G | 2km | SMF | 1310nm | Duplex | N | CWDM | ||
| 200GBase-LR4 | 200G | 50G | 10km | SMF | 1310nm | Duplex | N | LWDM | ||
| 2018 Jun | MSA ETC | 400GBase-KR8 | 400G | 50G | 1m | Backplane | Parallel | Y | ||
| 400GBase-CR8 | 400G | 50G | 5m | Copper | Parallel | Y | ||||
| 2018 Sep | MSA 100G LD | 100G-FR | 100G | 100G | 2km | SMF | 1310nm | Duplex | N | |
| 100G-LR | 100G | 100G | 10km | SMF | 1310nm | Duplex | N | |||
| 400G-FR4 | 400G | 100G | 2km | SMF | 1310nm | Duplex | N | CWDM | ||
| 400G-LR4-10 | 400G | 100G | 10km | SMF | 1310nm | Duplex | N | CWDM | ||
| 2018 Dec | IEEE 802.3cd | 200GBase-KR4 | 200G | 50G | 1m | Backplane | Parallel | Y | ||
| 200GBase-CR4 | 200G | 50G | 5m | Copper | Parallel | Y | ||||
| 200GBase-SR4 | 200G | 50G | 100m | MMF OM4 | 850nm | Parallel | Y | |||
| 100GBase-KR2 | 100G | 50G | 1m | Backplane | Parallel | Y | ||||
| 100GBase-CR2 | 100G | 50G | 5m | Copper | Parallel | Y | ||||
| 100GBase-SR2 | 100G | 50G | 100m | MMF OM4 | 850nm | Parallel | Y | |||
| 100GBase-DR | 100G | 100G | 500m | SMF | 1310nm | Duplex | N | |||
| 2019 Mar | MSA SWDM | 100G-SWDM2 | 100G | 50G | 100m | MMF OM4 | 850nm | Duplex | N | SWDM Bidi |
| 2019 Nov | IEEE 802.3cn | 400GBase-ER8 | 400G | 50G | 40km | SMF | 1310nm | Duplex | N | LWDM |
| 200GBase-ER4 | 200G | 50G | 40km | SMF | 1310nm | Duplex | N | LWDM | ||
| 2020 Jan | IEEE 802.3cm | 400GBase-SR8 | 400G | 50G | 100m | MMF OM4 | 850nm | Parallel | Y | |
| 400GBase-SR4.2 | 400G | 50G | 100m | MMF OM4 | 850nm | Parallel | Y | SWDM Bidi | ||
| 2020 Mar | MSA OIF | 400ZR | 400G | 400G | <120km | SMF | 1550nm | Duplex | Muxponder | Coherent |
| 2020 End | IEEE P802.3cu | 400GBase-FR4 | 400G | 100G | 2km | SMF | 1310nm | Duplex | N | CWDM |
| 400GBase-LR4-6 | 400G | 100G | 6km | SMF | 1310nm | Duplex | N | CWDM | ||
| 2020 End | MSA OpenZR+ | 400G-ZR+ | 400G | 400G | >120km | SMF | 1550nm | Duplex | Muxponder | Coherent |
| 2021 End | IEEE P802.3ck | 400GBase-CR4 | 400G | 100G | 5m | Copper | Parallel | Y | ||
| 200GBase-CR2 | 200G | 100G | 5m | Copper | Parallel | Y | ||||
| 100GBase-CR | 100G | 100G | 5m | Copper | Duplex | N | ||||
| 2021 End | IEEE P802.3ct | 100GBase-ZR | 100G | 100G | 80km | SMF | 1550nm | Duplex | N | Coherent |
| 2022 Mid | IEEE P802.3cw | 400GBase-ZR | 400G | 400G | 80km | SMF | 1550nm | Duplex | N | Coherent |
| 2022 Mid | IEEE P802.3db | 400GBase-SR4 | 400G | 100G | 50m | MMF OM4 | 850nm | Parallel | Y | |
| 200GBase-SR2 | 200G | 100G | 50m | MMF OM4 | 850nm | Parallel | y | |||
| 100GBase-SR | 100G | 100G | 50m | MMF OM4 | 850nm | Duplex | N |
NCS-5700 400G Optics Support and Roadmap
The whole new generation of 400G optics support will be introduced in phases for NCS-5700.
NCS-5700 QSFP-DD 400G Optics with 50G/100G PAM4 Wavelengths Support and Roadmap
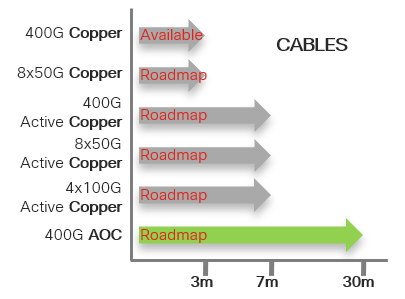
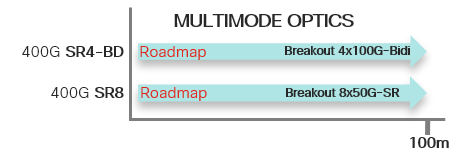
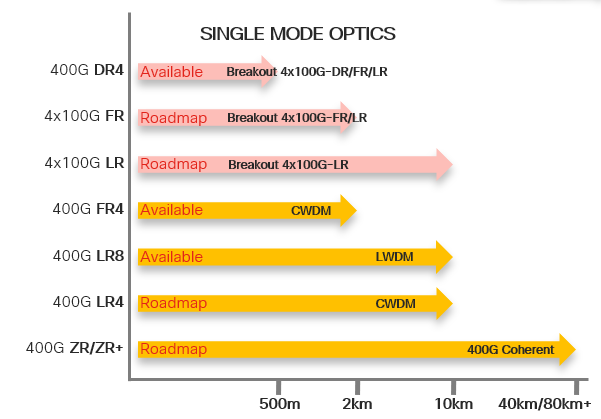
This section will cover all 400G optics with new generation 50G and 100G wavelengths, and using QSFP-DD form factor, that is available or under roadmap. More optics will be planned as and when they become available.
For ease of visualizing the use case of each optics, we have organized the optics into three major categories, each with varying distances and breakout capabilities.
Cables: Usually comes in passive copper Direct Attach Cables (DAC) for a few meters, or active optical cables (AOC) up to 30m. It could be direct, or breakout like 8x50 or 4x100.
Multimode Fibers: Usually Parallel MMF up to about 100m for OM4, and capable of breakout.
Single mode Fibers: Could be parallel SMF or duplex SMF. Parallel SMF is capable of breakout, and Duplex SMF will need WDM for multiplexing multiple wavelengths into a single SMF.
Please note for the supported 4x100G breakout, the remote end need to be a new generation 100G optics supporting 100G PAM4 wavelength. For example, 400GBase-DR4 supports 4x100G breakout to 4 remote 100G-DR/FR/LR.
Below charts will show currently available optics as of IOS XR 7.0.2. Releases for optics in roadmap will be announced when they become available.
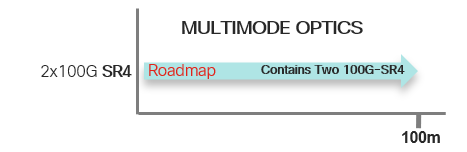
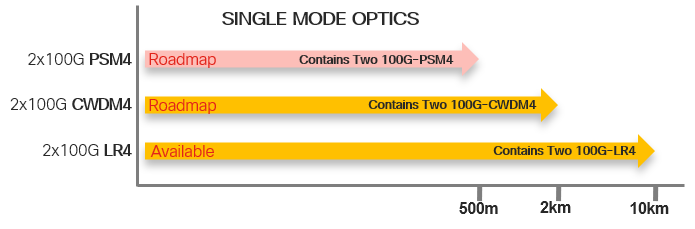
NCS-5700 QSFP28-DD 2x100G Optics with 25G NRZ Wavelengths Support and Roadmap
In current deployments, there are a lot of current generation QSFP28 optics with 4x 25G NRZ wavelengths.
There is therefore a need for higher density support of these optics on the new NCS-5700 linecards, in order to be backward compatible with currently deployed QSFP28 optics.
Current technology could support packaging 2 current generation QSFP28 optics in a single QSFP-DD form factor, therefore we will support a new generation of high density 2x100G optics with QSFP28-DD on the NCS-5700.
For ease of visualizing the use case of each optics, we have organized the optics into two major categories, each with varying distances and breakout capabilities.
Multimode Fibers: Usually Parallel MMF up to about 100m for OM4, and capable of breakout.
Single mode Fibers: Could be parallel SMF or duplex SMF. Parallel SMF is capable of breakout, and Duplex SMF will need WDM for multiplexing multiple wavelengths into a single SMF.
Below charts will show currently available optics as of IOS XR 7.0.2. Releases for optics in roadmap will be announced when they become available.
As there is limited face plate space on the QSFP-DD package, the 2x100G dual optics will require higher density connectors, such as MPO-24 for parallel optics, and Dual Duplex CS Connectors for duplex optics.
NCS-5700 QSFP28 100G Optics with New Generation 50G/100G PAM4 Wavelengths Support and Roadmap
As we gradually migrate to 400G optics, with new generation 50G/100G wavelengths, we also need the currently deployed 100GE ports to migrate to new generation optics with 50G/100G wavelengths.
This section will cover all 100G optics with new generation 50G and 100G wavelengths using QSFP28 form factor.
Exception will be 100G-ZR coherent optics, which requires higher power, so will only be supported on QSFP-DD form factor.
Below charts will show currently available optics as of IOS XR 7.0.2. Releases for optics in roadmap will be announced when they become available.
Summary of Optics PIDs and Roadmap
This is a summary table for 400G and related 100G optics availability and roadmap for NCS-5700 Linecards, NC55-24DD and NC57-18DD-SE for your reference, valid as of currently available IOS XR 7.0.2 release.
| PID | Description | Distance | Target FCS |
|---|---|---|---|
| QDD-400-CUxM | 400G QSFP-DD to QSFP-DD Passive Copper Cable 1/2 m | x m | 7.0.2 |
| QDD-400G-DR4-S | 400G QSFP-DD Transceiver, 400GBASE-DR4, MPO-12, SMF | 500 m | 7.0.2 |
| Can be used as 4x100G breakout to QSFP-100G-FR/LR-S | 500 m | Roadmap | |
| QDD-400G-FR4-S | 400G QSFP-DD Transceiver, 400GBASE-FR4, Duplex LC, SMF | 2 km | 7.0.2 |
| QDD-400G-LR8-S | 400G QSFP-DD Transceiver, 400GBASE-LR8, Duplex LC, SMF | 10 km | 7.0.2 |
| QDD-2X100-LR4-S | 2x100G QSFP-DD Transceiver, 2x100GBASE-LR4, Dual Duplex CS, SMF | 10 km | 7.0.2 |
| QDD-2X100-CWDM4-S | 2x100G QSFP-DD Transceiver, 2x100G-CWDM4, Dual Duplex CS, SMF | 2 km | Roadmap |
| QDD-2X100-SR4-S | 2x100G QSFP-DD Transceiver, 2x100GBASE-SR4, MPO-24, MMF, OM4 | 100 m | Roadmap |
| QDD-2x100-PSM4-S | 2x100G QSFP-DD Transceiver, 2x100G-PSM4, MPO-24, SMF | 500 m | Roadmap |
| QSFP-40/100-SRBD | Dual Rate QSFP28 Transceiver, 100G-SWDM2 Bidi , Duplex LC, MMF, OM4 | 100 m | Roadmap |
| QSFP-100G-DR-S | 100G QSFP28 Transceiver, 100GBASAE-DR, SMF, Duplex LC, SMF | 500 m | Roadmap |
| QSFP-100G-FR-S | 100G QSFP28 Transceiver, 100GBASAE-FR, SMF, Duplex LC, SMF | 2 km | Roadmap |
| QSFP-100G-LR-S | 100G QSFP28 Transceiver, 100GBASAE-LR, SMF, Duplex LC, SMF | 10 km | Roadmap |
| QDD-4x100G-FR | 4x100G QSFP-DD Transceiver, 4x100GBASE-FR, MPO-12, SMF | 2 km | Roadmap |
| Can be used as 4x100G breakout to QSFP-100G-FR/LR-S | 2 km | Roadmap | |
| QDD-4x100G-LR | 4x100G QSFP-DD Transceiver, 4x100GBASE-LR, MPO-12, SMF | 10 km | Roadmap |
| Can be used as 4x100G breakout to QSFP-100G-LR-S | 10 km | Roadmap | |
| QDD-400G-SR4-BD | 400G QSFP-DD Transceiver, 400GBASE-SR4.2, MPO-12, MMF, OM4 | 100 m | Roadmap |
| Can be used as 4x100G breakout to 100G-SWDM2 BiDi | 100 m | Roadmap | |
| QDD-400G-SR8-S | 400G QSFP-DD Transceiver, 400GBASE-SR8, MPO-16, MMF, OM4 | 100 m | Roadmap |
| Can be used as 8x50G breakout to 50GBASE-SR | 100 m | Roadmap | |
| QDD-400G-LR4-S | 400G QSFP-DD Transceiver, 400G-LR4, SMF, Duplex LC, SMF | 10 km | Roadmap |
| QDD-400G-ZR-S | 400G QSFP-DD Transceiver, OIF 400ZR, Tunable Coherent, Duplex LC, SMF (requires EDFA for links in excess of 40km) | 80 km+ (120 km max) | Roadmap |
| QDD-400G-ZRP-S | 100G/200G/300G/400G QSFP-DD Transceiver, 400G-ZR+, Tunable Coherent Duplex LC, SMF (requires EDFA for links in excess of 40km - 400G) | 1200 km+ | Roadmap |
| QDD-100G-ZR | 100G QSFP-DD Transceiver, Tunable Coherent, Duplex LC, SMF | 80 km+ (120 km max) | Roadmap |

Leave a Comment