XR Toolbox, Part 3 : App Development Topology
Check out Part 2 of the XR toolbox series: Bootstrap XR configuration with Vagrant.
Introduction
Without diving too deep into the IOS-XR architecture, it might be useful to state that applications on IOS-XR may be deployed in two different ways:
- natively (inside the XR process space) OR
- as a container (LXC)
In this quick start guide we introduce a typical vagrant topology that we intend to use in other quick start guides in the XR Toolbox series.
This topology will be used to build and deploy container (LXC) as well as native XR applications and test them on Vagrant IOS-XR.
Pre-requisites
- Meet the pre-requisites specified in the IOS-XR Vagrant Quick Start guide: Pre-requisites.
The topology here will require about 5G RAM and 2 cores on the user’s laptop. - Clone the following repository: https://github.com/ios-xr/vagrant-xrdocs, before we start.
cd ~/
git clone https://github.com/ios-xr/vagrant-xrdocs.git
cd vagrant-xrdocs/
You will notice a few directories. We will utilize the lxc-app-topo-bootstrap directory in this tutorial.
AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant-xrdocs akshshar$ pwd
/Users/akshshar/vagrant-xrdocs
AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant-xrdocs akshshar$ ls lxc-app-topo-bootstrap/
Vagrantfile configs scripts
AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant-xrdocs akshshar$
Understand the topology
For this tutorial, we’ll use a two-node topology: An XR vagrant instance connected to Linux instance (devbox). For illustrative purposes, we use Ubuntu as our devbox OS:
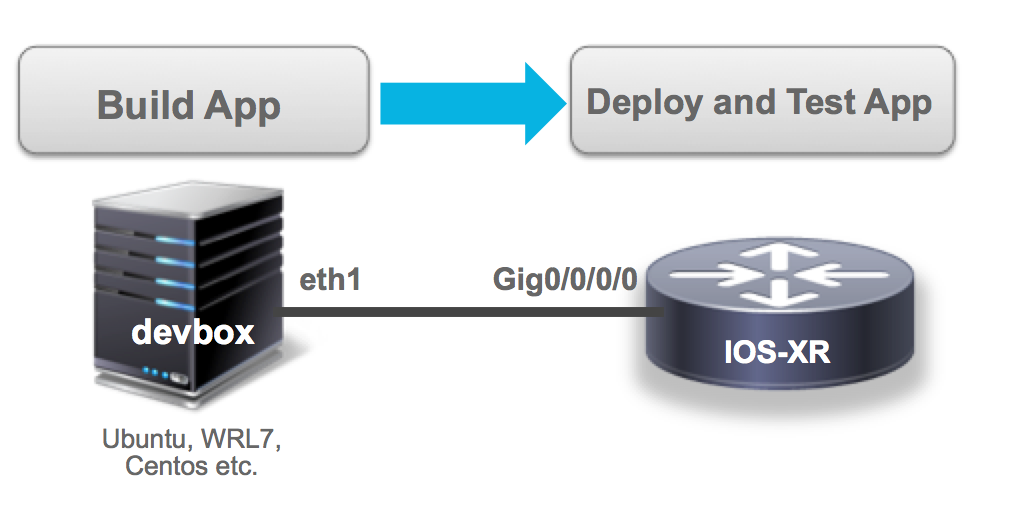
The Vagrantfile to bring up this topology is already in your cloned directory:
vagrant-xrdocs/lxc-app-topo-bootstrap/Vagrantfile
Vagrant.configure(2) do |config|
config.vm.define "rtr" do |node|
node.vm.box = "IOS-XRv"
# gig0/0/0 connected to "link1"
# auto_config is not supported for XR, set to false
node.vm.network :private_network, virtualbox__intnet: "link1", auto_config: false
#Source a config file and apply it to XR
node.vm.provision "file", source: "configs/rtr_config", destination: "/home/vagrant/rtr_config"
node.vm.provision "shell" do |s|
s.path = "scripts/apply_config.sh"
s.args = ["/home/vagrant/rtr_config"]
end
end
config.vm.define "devbox" do |node|
node.vm.box = "ubuntu/trusty64"
# eth1 connected to link1
# auto_config is supported for an ubuntu instance
node.vm.network :private_network, virtualbox__intnet: "link1", ip: "11.1.1.20"
end
end
Notice the #Source a config file and apply it to XR section of the Vagrantfile? This is derived from the Bootstrap XR configuration with Vagrant tutorial. Check it out if you want to know more about how shell provisioning with XR works
The configuration we wish to apply to XR on boot is pretty simple. You can find it in the lxc-app-topo-bootstrap/configs directory.
We want to configure the XR interface: GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 with the ip-address: 11.1.1.10
AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant-xrdocs akshshar$ cat lxc-app-topo-bootstrap/configs/rtr_config
!! XR configuration
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0
ip address 11.1.1.10/24
no shutdown
!
end
AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:vagrant-xrdocs akshshar$
Take a look at the Vagrantfile above, again. We use the Vagrant auto_config capabilities to make sure “eth1” interface of the Ubuntu VM (called devbox) is configured in the same subnet (11.1.1.20) as XR gig0/0/0/0.
Bring up the topology
Download and Add the XR Vagrant box
IOS-XR Vagrant is currently in Private Beta
To download the box, you will need an API-KEY and a CCO-ID
To get the API-KEY and a CCO-ID, browse to the following link and follow the steps:
$ BOXURL="http://devhub.cisco.com/artifactory/appdevci-release/XRv64/latest/iosxrv-fullk9-x64.box"
$ curl -u your-cco-id:API-KEY $BOXURL --output ~/iosxrv-fullk9-x64.box
$ vagrant box add --name IOS-XRv ~/iosxrv-fullk9-x64.box
Of course, you should replace your-cco-id with your actual Cisco.com ID and API-KEY with the key you generated and copied using the above link.
The vagrant box add command will take around 10-15 mins as it downloads the box for you.
Once it completes, you should be able to see the box added as “IOS-XRv” in your local vagrant box list:
AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:~ akshshar$ vagrant box list
IOS-XRv (virtualbox, 0)
AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:~ akshshar$
Launch the nodes
Make sure you’re in the lxc-app-topo-bootstrap/ directory and issue a vagrant up
AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:lxc-app-topo-bootstrap akshshar$pwd
/Users/akshshar/vagrant-xrdocs/lxc-app-topo-bootstrap
AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:lxc-app-topo-bootstrap akshshar$ vagrant up
Bringing machine 'rtr' up with 'virtualbox' provider...
Bringing machine 'devbox' up with 'virtualbox' provider...
==> rtr: Importing base box 'IOS-XRv'...
==> rtr: Matching MAC address for NAT networking...
==> rtr: Setting the name of the VM: lxc-app-topo-bootstrap_rtr_1465208784531_75603
==> rtr: Clearing any previously set network interfaces...
==> rtr: Preparing network interfaces based on configuration...
rtr: Adapter 1: nat
rtr: Adapter 2: intnet
==> rtr: Forwarding ports...
rtr: 57722 (guest) => 2222 (host) (adapter 1)
rtr: 22 (guest) => 2223 (host) (adapter 1)
==> rtr: Running 'pre-boot' VM customizations...
==> rtr: Booting VM...
==> rtr: Waiting for machine to boot. This may take a few minutes...
rtr: SSH address: 127.0.0.1:2222
rtr: SSH username: vagrant
rtr: SSH auth method: private key
rtr: Warning: Remote connection disconnect. Retrying...
rtr: Warning: Remote connection disconnect. Retrying...
Once it completes, you should be able to see both the VMs running by using the vagrant status command inside the lxc-app-topo-bootstrap/ directory:
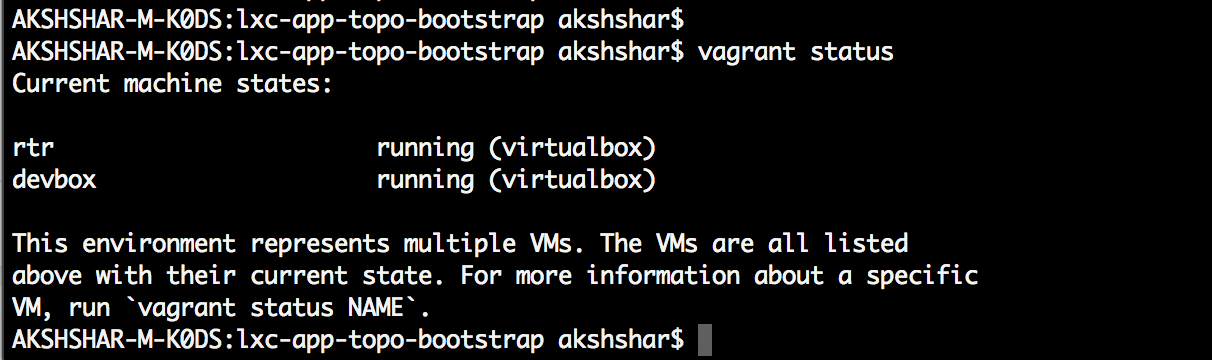
Check Reachability
To get into the Ubuntu “devbox”, issue a vagrant ssh devbox:
AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:lxc-app-topo-bootstrap akshshar$ vagrant ssh devbox
Welcome to Ubuntu 14.04.4 LTS (GNU/Linux 3.13.0-87-generic x86_64)
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com/
System information as of Mon Jun 6 11:20:37 UTC 2016
System load: 0.0 Processes: 74
Usage of /: 3.5% of 39.34GB Users logged in: 0
Memory usage: 25% IP address for eth0: 10.0.2.15
Swap usage: 0% IP address for eth1: 11.1.1.20
Graph this data and manage this system at:
https://landscape.canonical.com/
Get cloud support with Ubuntu Advantage Cloud Guest:
http://www.ubuntu.com/business/services/cloud
0 packages can be updated.
0 updates are security updates.
vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~$
From “devbox”, you should be able to ping the XR Gig0/0/0/0 interface:
vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~$ ping 11.1.1.10 -c 2
PING 11.1.1.10 (11.1.1.10) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 11.1.1.10: icmp_seq=1 ttl=255 time=1.56 ms
64 bytes from 11.1.1.10: icmp_seq=2 ttl=255 time=1.44 ms
--- 11.1.1.10 ping statistics ---
2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 1003ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 1.447/1.504/1.562/0.069 ms
vagrant@vagrant-ubuntu-trusty-64:~$
To get into XR linux shell, issue vagrant ssh rtr
AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:lxc-app-topo-bootstrap akshshar$ vagrant ssh rtr
Last login: Mon Jun 6 11:20:58 2016 from 10.0.2.2
xr-vm_node0_RP0_CPU0:~$
xr-vm_node0_RP0_CPU0:~$ifconfig Gi0_0_0_0
Gi0_0_0_0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:46:1f:b2
inet addr:11.1.1.10 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::a00:27ff:fe46:1fb2/64 Scope:Link
UP RUNNING NOARP MULTICAST MTU:1514 Metric:1
RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:1 errors:0 dropped:3 overruns:0 carrier:1
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:42 (42.0 B)
xr-vm_node0_RP0_CPU0:~$
xr-vm_node0_RP0_CPU0:~$
xr-vm_node0_RP0_CPU0:~$
To get into XR CLI, remember that XR SSH runs on port 22 of the guest IOS-XR instance.
First, determine the port to which the XR SSH port (port 22) is forwarded by vagrant by using the vagrant port command:
AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:lxc-app-topo-bootstrap akshshar$ vagrant port rtr
The forwarded ports for the machine are listed below. Please note that
these values may differ from values configured in the Vagrantfile if the
provider supports automatic port collision detection and resolution.
22 (guest) => 2223 (host)
57722 (guest) => 2222 (host)
As shown above, port 22 of XR is fowarded to port 2223:
Use port 2223 to now ssh into XR CLI
The password is “vagrant”
AKSHSHAR-M-K0DS:lxc-app-topo-bootstrap akshshar$ ssh -p 2223 vagrant@localhost
The authenticity of host '[localhost]:2223 ([127.0.0.1]:2223)' can't be established.
RSA key fingerprint is 7f:1a:56:e1:3c:7f:cf:a4:ee:ac:20:3a:e6:cf:ad:f5.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
Warning: Permanently added '[localhost]:2223' (RSA) to the list of known hosts.
vagrant@localhost's password:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios#
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios#show ipv4 interface gigabitEthernet 0/0/0/0 brief
Tue Jun 7 03:23:31.324 UTC
Interface IP-Address Status Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 11.1.1.10 Up Up
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:ios#
You’re all set! You can now use this topology to build applications (native-WRL7 or LXC containers) on the “devbox” and test them out on the IOS-XR vagrant node. We will explore these scenarios in the next set of tutorials in the XR Toolbox series.
Head over to Part 4 of the XR Toolbox series where we create and bring up a container (LXC) app on IOS-XR —> Bring your own Container (LXC) App.
Leave a Comment